This is a preprint.
Comparative modeling reveals the molecular determinants of aneuploidy fitness cost in a wild yeast model
- PMID: 38645209
- PMCID: PMC11030387
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.04.09.588778
Comparative modeling reveals the molecular determinants of aneuploidy fitness cost in a wild yeast model
Update in
-
Comparative modeling reveals the molecular determinants of aneuploidy fitness cost in a wild yeast model.Cell Genom. 2024 Oct 9;4(10):100656. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2024.100656. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Cell Genom. 2024. PMID: 39317188 Free PMC article.
Abstract
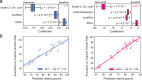
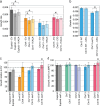
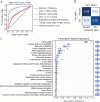
Although implicated as deleterious in many organisms, aneuploidy can underlie rapid phenotypic evolution. However, aneuploidy will only be maintained if the benefit outweighs the cost, which remains incompletely understood. To quantify this cost and the molecular determinants behind it, we generated a panel of chromosome duplications in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and applied comparative modeling and molecular validation to understand aneuploidy toxicity. We show that 74-94% of the variance in aneuploid strains' growth rates is explained by the additive cost of genes on each chromosome, measured for single-gene duplications using a genomic library, along with the deleterious contribution of snoRNAs and beneficial effects of tRNAs. Machine learning to identify properties of detrimental gene duplicates provided no support for the balance hypothesis of aneuploidy toxicity and instead identified gene length as the best predictor of toxicity. Our results present a generalized framework for the cost of aneuploidy with implications for disease biology and evolution.
Keywords: Aneuploidy; Balance hypothesis; CNV; dosage-sensitive genes; snoRNA; tRNA.
Figures



References
-
- Hassold T. & Hunt P. To err (meiotically) is human: the genesis of human aneuploidy. Nat Rev Genet 2, 280–291 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
