This is a preprint.
Expression of c-erb-B2 oncoprotein as a neoantigen strategy to repurpose anti-neu antibody therapy in a model of melanoma
- PMID: 38645250
- PMCID: PMC11030526
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4004491/v1
Expression of c-erb-B2 oncoprotein as a neoantigen strategy to repurpose anti-neu antibody therapy in a model of melanoma
Update in
-
Expression of c-erb-B2 oncoprotein as a neoantigen strategy to repurpose anti-neu antibody therapy in a model of melanoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 19;14(1):24545. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76209-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39427012 Free PMC article.
Abstract
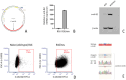
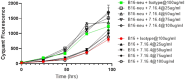
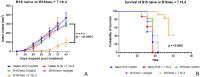
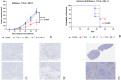
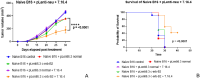
In this study, we tested a novel approach of "repurposing" a biomarker typically associated with breast cancer for use in melanoma. HER2/neu is a well characterized biomarker in breast cancer for which effective anti-HER2/neu therapies are readily available. We constructed a lentivirus encoding c-erb-B2 (the animal homolog to HER2/neu). This was used to transfect B16 melanoma in vitro for use in an orthotopic preclinical mouse model, which resulted in expression of c-erb-B2 as a neoantigen target for anti-c-erb-B2 monoclonal antibody (7.16.4). The c-erb-B2-expressing melanoma was designated B16/neu. 7.16.4 produced statistically significant in vivo anti-tumor responses against B16/neu. This effect was mediated by NK-cell antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. To further model human melanoma (which expresses <5% HER2/neu), our c-erb-B2 encoding lentivirus was used to inoculate naïve (wild-type) B16 tumors in vivo, resulting in successful c-erb-B2 expression. When combined with 7.16.4, anti-tumor responses were again demonstrated where approximately 40% of mice treated with c-erb-B2 lentivirus and 7.16.4 achieved complete clinical response and long-term survival. For the first time, we demonstrated a novel strategy to repurpose c-erb-B2 as a neoantigen target for melanoma. Our findings are particularly significant in the contemporary setting where newer anti-HER2/neu antibody-drug candidates have shown increased efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures There are no financial disclosures, competing interests, or conflicts of interest for this manuscript for any of the listed authors. The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of c-erb-B2 oncoprotein as a neoantigen strategy to repurpose anti-neu antibody therapy in a model of melanoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 19;14(1):24545. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76209-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39427012 Free PMC article.
-
C-erb B2 (Her2/neu) is neither overexpressed nor amplified in hepatic neoplasms.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2002 Sep;10(3):237-41. doi: 10.1097/00129039-200209000-00009. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2002. PMID: 12373150
-
Enhanced pancreatic cancer gene therapy by combination of adenoviral vector expressing c-erb-B2 (Her-2/neu)-targeted immunotoxin with a replication-competent adenovirus or etoposide.Hum Gene Ther. 2010 Feb;21(2):157-70. doi: 10.1089/hum.2009.083. Hum Gene Ther. 2010. PMID: 19751100
-
Profiling serum HER-2/NEU in prostate cancer.Hippokratia. 2013 Apr;17(2):108-12. Hippokratia. 2013. PMID: 24376312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunobiology of HER-2/neu oncoprotein and its potential application in cancer immunotherapy.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2004 Mar;53(3):166-75. doi: 10.1007/s00262-003-0475-7. Epub 2003 Dec 18. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2004. PMID: 14685781 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marei H. E., Hasan A., Pozzoli G. & Cenciarelli C. Cancer immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs): potential, mechanisms of resistance, and strategies for reinvigorating T cell responsiveness when resistance is acquired. Cancer cell international 23, 64, doi:10.1186/s12935-023-02902-0 (2023). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

