Novel drugs affecting diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- PMID: 38645500
- PMCID: PMC11024403
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2024.75367.16334
Novel drugs affecting diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Abstract
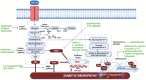
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) poses a significant threat, affecting half of the global diabetic population and leading to severe complications, including pain, impaired mobility, and potential amputation. The delayed manifestation of diabetic neuropathy (DN) makes early diagnosis challenging, contributing to its debilitating impact on individuals with diabetes mellitus (DM). This review examines the multifaceted nature of DPN, focusing on the intricate interplay between oxidative stress, metabolic pathways, and the resulting neuronal damage. It delves into the challenges of diagnosing DN, emphasizing the critical role played by hyperglycemia in triggering these cascading effects. Furthermore, the study explores the limitations of current neuropathic pain drugs, prompting an investigation into a myriad of pharmaceutical agents tested in both human and animal trials over the past decade. The methodology scrutinizes these agents for their potential to provide symptomatic relief for DPN. The investigation reveals promising results from various pharmaceutical agents tested for DPN relief, showcasing their efficacy in ameliorating symptoms. However, a notable gap persists in addressing the underlying problem of DPN. The results underscore the complexity of DPN and the challenges in developing therapies that go beyond symptomatic relief. Despite advancements in treating DPN symptoms, there remains a scarcity of options addressing the underlying problem. This review consolidates the state-of-the-art drugs designed to combat DPN, highlighting their efficacy in alleviating symptoms. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for a deeper understanding of the diverse processes and pathways involved in DPN pathogenesis.
Keywords: Diabetic peripheral- neuropathy; Hyperglycemia; Molecular mechanism; Neuropathic pain; Quality of life; Therapeutic targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Diabetic painful neuropathy: current and future treatment options.Drugs. 2007;67(4):569-85. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200767040-00006. Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17352515 Review.
-
L-Methylfolate in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Narrative Review.Endocr Pract. 2023 Aug;29(8):663-669. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2023.04.005. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Endocr Pract. 2023. PMID: 37088147 Review.
-
Axonal transport deficits in the pathogenesis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 28;14:1136796. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1136796. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37056668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroinflammation in diabetic peripheral neuropathy and therapeutic implications.Rev Neurosci. 2025 Apr 16. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2025-0031. Online ahead of print. Rev Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40228523 Review.
-
New Perspective in Diabetic Neuropathy: From the Periphery to the Brain, a Call for Early Detection, and Precision Medicine.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Jan 17;10:929. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00929. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32010062 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maltol Improves Peripheral Nerve Function by Inhibiting Schwann Cell Apoptosis via the PERK/eIF2α/CHOP Pathway and MME Upregulation in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 29;17(9):1139. doi: 10.3390/ph17091139. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oliver TI, Mutluoglu M. Diabetic Foot Ulcer. StatPearls: Treasure Island (FL); 2022. - PubMed
-
- A Sedik A. Modulation activity of vildagliptin on hepatic complications and lipoprotein abnormalities associated with insulin resistance in rats. Egypt J Chem. 2022;65:541–547.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
