Photonic control of image-guided ferroptosis cancer nanomedicine
- PMID: 38645709
- PMCID: PMC11027759
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215532
Photonic control of image-guided ferroptosis cancer nanomedicine
Abstract
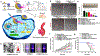
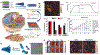
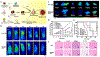
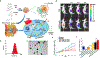
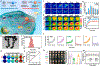
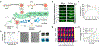
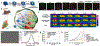
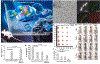
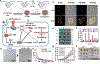
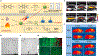
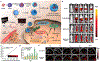
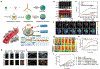
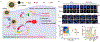
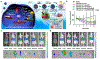
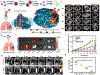
Photonic nanomaterials, characterized by their remarkable photonic tunability, empower a diverse range of applications, including cutting-edge advances in cancer nanomedicine. Recently, ferroptosis has emerged as a promising alternative strategy for effectively killing cancer cells with minimizing therapeutic resistance. Novel design of photonic nanomaterials that can integrate photoresponsive-ferroptosis inducers, -diagnostic imaging, and -synergistic components provide significant benefits to effectively trigger local ferroptosis. This review provides a comprehensive overview of recent advancements in photonic nanomaterials for image-guided ferroptosis cancer nanomedicine, offering insights into their strengths, constraints, and their potential as a future paradigm in cancer treatment.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Coordination nanomedicine; Ferroptosis; Image-guided therapy; Photonic nanomaterials.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


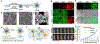

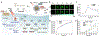
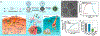


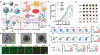
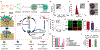
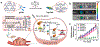

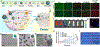


References
-
- Jin W, Fan B, Qin X, Liu Y, Qian C, Tang B, James TD, Chen G, Structure-activity of chlormethine fluorescent prodrugs: Witnessing the development of trackable drug delivery, Coord. Chem. Rev 480 (2023), 214999, 10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214999. - DOI
-
- Wu X, Macreadie LK, Gale PA, Anion binding in metal-organic frameworks, Coord. Chem. Rev 432 (2021), 213708, 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213708. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
