Building and Validation of an Acute Event Prediction Model for Severe Mental Disorders
- PMID: 38645710
- PMCID: PMC11032721
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S453838
Building and Validation of an Acute Event Prediction Model for Severe Mental Disorders
Abstract
Background: The global incidence of acute events in psychiatric patients is intensifying, and models to successfully predict acute events have attracted much attention.
Objective: To explore the influence factors of acute incident severe mental disorders (SMDs) and the application of Rstudio statistical software, and build and verify a nomogram prediction model.
Methods: SMDs were taken as research objects. The questionnaire survey method was adopted to collect data. Patients with acute event independent factors were screened. R software multivariable Logistic regression model was constructed and a nomogram was drawn.
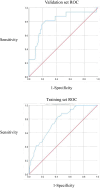
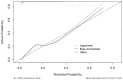
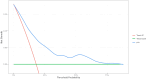
Results: A total of 342 patients with SMDs were hospitalized, and the number of patients who encountered acute events was 64, which accounted for 18.70% of all patients. Statistical significances were found in many aspects (all P ˂ 0.05). Such aspects included Medication adherence, disease diagnosis, marital status, caregivers, social support and the hospitalization environment (odds ratio (OR) = 4.08, 11.62, 12.06, 10.52, 0.04 and 0.61, respectively) were independent risk factors for the acute events of patients with SMDs. The prediction model was modeled, and the AUC was 0.77 and 0.80. The calibration curve shows that the model has good calibration. The clinical decision curve shows that the model has a good clinical effect.
Conclusion: The constructed risk prediction model shows good prediction effectiveness in the acute events of patients with SMDs, which is helpful for the early detection of clinical mental health staff at high risk of acute events.
Keywords: SMDs; acute event; influencing factors; predictive model and nomogram.
© 2024 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Wang Y, Li C, Song P. Analysis of death and life reduction of patients with severe mental disorders in Ningbo from 2016 to 2020. Preventive Med. 2022;34(12):1224–1229. doi:10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087.2022.12.007 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

