CyberKnife Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Uveal Melanoma: First Case Series in Central America
- PMID: 38645736
- PMCID: PMC11024490
- DOI: 10.1159/000534207
CyberKnife Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Uveal Melanoma: First Case Series in Central America
Abstract
Introduction: Uveal melanoma is the most common primary intraocular malignancy in adults, affecting primarily the choroid of the eye. Plaque brachytherapy is the most common procedure for the treatment of small choroidal melanoma, especially in posteriorly located tumors. However, modern radiotherapy techniques, such as CyberKnife or Gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and proton beam radiotherapy, have shown better results in tumor control and eye retention. Recent studies have indicated that SRS is a promising non-invasive, single-session treatment option, with most studies reporting the best outcomes when using ≥21-22 Gy. However, there is no consistent protocol for managing this pathology using CyberKnife, not only in terms of dose but also fractions.
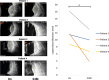
Case presentations: Here, we report the first case series of patients (n = 4, age range 38-64 years, median age 52.5 years) with choroidal UM in Central America who were treated with CyberKnife SRS (22 Gy in one session). During the follow-up (range 25-29 months, median 27.5 months), a 100% control rate with no systemic metastatic disease has been achieved. We found a statistically significant reduction in the largest basal diameter at 24 months for all tumors. However, visual acuity has progressively decreased in most patients. Notably, two of our patients developed radiation maculopathy, and the other two developed radiation retinopathy after SRS.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that future studies should evaluate the use of different prophylactic therapies to prevent the development of side effects. The clinical management of toxicities presented in our report can serve as a reference in the clinical practice of other centers. Our report supports the growing body of evidence showing that CyberKnife radiosurgery is a safe and effective therapeutic option for the treatment of UM.
Keywords: Choroidal melanoma; CyberKnife; Ocular oncology; Stereotactic radiosurgery; Uveal melanoma.
© 2023 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery for medium and large uveal melanoma with a non-invasive eye immobilization device, a single institutional case series.J Formos Med Assoc. 2023 Nov;122(11):1117-1124. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2023.04.013. Epub 2023 May 29. J Formos Med Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37258323
-
[CyberKnife®: new treatment option for uveal melanoma].Ophthalmologe. 2018 Apr;115(4):302-308. doi: 10.1007/s00347-017-0560-5. Ophthalmologe. 2018. PMID: 28849326 Review. German.
-
RADIATION MACULOPATHY AFTER ONE-DAY SESSION STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN PATIENTS WITH CILIARY BODY AND CHOROIDAL MELANOMA.Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2019 Spring;75(1):3-10. doi: 10.31348/2019/1/1. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2019. PMID: 31382751 English.
-
Robotic CyberKnife radiosurgery for small choroidal melanomas.Melanoma Res. 2022 Jun 1;32(3):192-199. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0000000000000823. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Melanoma Res. 2022. PMID: 35404316
-
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Uveal Metastases: Report of Three Cases and a Review of the Literature.Am J Ophthalmol. 2017 Feb;174:169-174. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2016.11.009. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Am J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 27889503 Review.
References
-
- Jager MJ, Shields CL, Cebulla CM, Abdel-Rahman MH, Grossniklaus HE, Stern M-H, et al. . Uveal melanoma. Nat Rev Dis Primer. 2020 Apr;6(1):24. - PubMed
-
- Shields CL, Kaliki S, Shah SU, Luo W, Furuta M, Shields JA. Iris melanoma: features and prognosis in 317 children and adults. J Am Assoc Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2012 Feb;16(1):10–6. - PubMed
-
- Damato EM, Damato BE. Detection and time to treatment of uveal melanoma in the United Kingdom: an evaluation of 2,384 patients. Ophthalmology. 2012 Aug;119(8):1582–9. - PubMed
-
- Kujala E, Mäkitie T, Kivelä T. Very long-term prognosis of patients with malignant uveal melanoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 Nov;44(11):4651–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

