DNA metabarcoding reveals the seasonal variation of dietary composition of Taihangshan macaque (Macaca mulatta tcheliensis), Jiyuan, north China
- PMID: 38646002
- PMCID: PMC11027012
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.11256
DNA metabarcoding reveals the seasonal variation of dietary composition of Taihangshan macaque (Macaca mulatta tcheliensis), Jiyuan, north China
Abstract
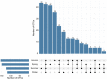
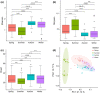
Dietary analysis in wildlife is fundamental for understanding their flexible response to seasonal changes and developing effective conservation management measures. Taihangshan macaque (Macaca mulatta tcheliensis) is the northernmost population of rhesus macaque, currently only distributed in the southern Mt. Taihangshan area. This area belongs to a semi-arid region resulting in limited plant food availability for Taihangshan macaques, with seasonal variation. Herein, we used a chloroplast trnL DNA metabarcoding approach to identify the plant diet diversity and composition from 100 fecal samples of Taihangshan macaque in four seasons (spring, summer, autumn, and winter) from 2020 to 2021. The results revealed that (1) a total of 48 distinct families, 88 genera, and 52 species within the 105 food items that were consumed by Taihangshan macaques throughout the year; (2) the diversity of food items exhibited significant differences across the four seasons; (3) Rosaceae, Rhamnaceae, Fagaceae, and Poaceae are the preferential food items for Taihangshan macaques and have different relative abundances, fluctuating with seasonal variation. DNA metabarcoding can expand our understanding of the repertoire of food items consumed by Taihangshan macaques by detecting some consumed food items in this population that were not yet discovered using traditional methods. Therefore, the integrative results from traditional methods and DNA metabarcoding can provide a fundamental understanding of dietary composition to guide the conservation management of Taihangshan macaques.
Keywords: DNA metabarcoding; Taihangshan macaque (Macaca mulatta tcheliensis); dietary composition; dietary diversity; seasonal variation.
© 2024 The Authors. Ecology and Evolution published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Browett, S. S. , Synnott, R. , O'Meara, D. B. , Antwis, R. E. , Browett, S. S. , Bown, K. J. , Wangensteen, O. S. , Dawson, D. A. , Searle, J. B. , Yearsley, J. M. , & McDevitt, A. D. (2023). Resource competition drives an invasion‐replacement event among shrew species on an Island. Journal of Animal Ecology, 92(3), 698–709. 10.1111/1365-2656.13855 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cabodevilla, X. , Mougeot, F. , Bota, G. , Manosa, S. , Cusco, F. , Martinez‐Garcia, J. , Arroyo, B. , & Madeira, M. J. (2021). Metabarcoding insights into the diet and trophic diversity of six declining farmland birds. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 21131. 10.1038/s41598-021-00519-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caporaso, J. G. , Kuczynski, J. , Stombaugh, J. , Bittinger, K. , Bushman, F. D. , Costello, E. K. , Fierer, N. , Peña, A. G. , Goodrich, J. K. , Gordon, J. I. , Huttley, G. A. , Kelley, S. T. , Knights, D. , Koenig, J. E. , Ley, R. E. , Lozupone, C. A. , McDonald, D. , Muegge, B. D. , Pirrung, M. , … Knight, R. (2010). QIIME allows analysis of high‐throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods, 7(5), 335–336. 10.1038/nmeth.f.303 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, W. (2021). Soil respiration and its temperature sensitivity of different vegetation types at southern foothil of Taihang Mountains. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 41(2), 92–98.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

