Global, regional, and national burden of pancreatitis in older adults, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019
- PMID: 38646072
- PMCID: PMC11026839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2024.102722
Global, regional, and national burden of pancreatitis in older adults, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019
Abstract
Background: To describe the past, present and future burden of pancreatitis in older adults, and to explore cross-national inequalities across socio-demographic index (SDI).
Methods: Data on pancreatitis in older adults, including mortality and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) rates, were collected from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2019 study. Temporal trends were measured using joinpoint analyses and predicted using a Bayesian age-period-cohort model. Additionally, the unequal distribution of the burden of pancreatitis in older adults was quantified.
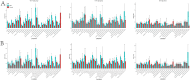
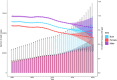
Results: From 1990 to 2019, the number of deaths and DALYs due to pancreatitis in older adults has been increasing annually. However, in most regions of the world, age-standardized death rates (ASDR) and age-standardized DALYs rates have been declining. The burden of pancreatitis in older adults was highest in low SDI region, primarily affecting the population aged 65-74, with a greater burden on males than females. Furthermore, from 1990 to 2019, absolute and relative cross-national inequalities in pancreatitis among older adults have remained largely unchanged. It is projected that in the next 11 years, the number of deaths in older adults due to pancreatitis will continue to increase, but the ASDR is expected to decline.
Conclusion: Over the past 30 years, the ASDR and age-standardized DALYs rate of pancreatitis in older adults have shown a decline globally, but the absolute burden continues to increase. Cross-national health inequalities persist. Therefore, it is necessary to develop targeted intervention measures and enhance awareness among this vulnerable population regarding the risk factors associated with pancreatitis.
Keywords: Cross-national inequalities; Global burden of disease; Joinpoint analysis; Older adult; Pancreatitis.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
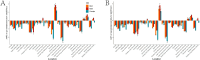
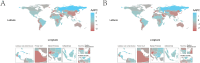

References
-
- Bang J.Y., Arnoletti J.P., Holt B.A., Sutton B., Hasan M.K., Navaneethan U., Feranec N., Wilcox C.M., Tharian B., Hawes R.H., et al. An Endoscopic Transluminal Approach, Compared With Minimally Invasive Surgery, Reduces Complications and Costs for Patients With Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(4):1027–1040. - PubMed
-
- Baron T.H., DiMaio C.J., Wang A.Y., Morgan K.A. American Gastroenterological Association Clinical Practice Update: Management of Pancreatic Necrosis. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(1):67–75. - PubMed
-
- Bottazzi B., Riboli E., Mantovani A. Aging, inflammation and cancer. Semin Immunol. 2018;40:74–82. - PubMed
-
- Boxhoorn L., Voermans R.P., Bouwense S.A., Bruno M.J., Verdonk R.C., Boermeester M.A., van Santvoort H.C., Besselink M.G. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 2020;396(10252):726–734. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

