Bidirectional correlation between gastroesophageal reflux disease and sleep problems: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38646475
- PMCID: PMC11027907
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.17202
Bidirectional correlation between gastroesophageal reflux disease and sleep problems: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and sleep problems are highly prevalent among the general population. Both them are associated with a variety of psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety, which is highlighting an underexplored connection between them. This meta-analysis aims to explore the association between sleep problems and GERD.
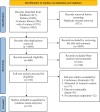
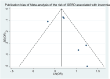
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search on PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, and Web of Science, using Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and keywords, covering articles from the inception of the databases until August 2023. Stata statistical software, version 14.0, was utilized for all statistical analyses. A fixed-effects model was applied when p > 0.1 and I2 ≤ 50%, while a random-effects model was employed for high heterogeneity (p < 0.1 and I2 > 50%). Funnel plots and Egger's test were used to assess publication bias.
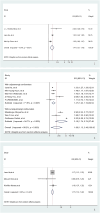
Results: Involving 22 studies, our meta-analysis revealed that insomnia, sleep disturbance, or short sleep duration significantly increased the risk of GERD (OR = 2.02, 95% CI [1.64-2.49], p < 0.001; I2 = 66.4%; OR = 1.98, 95% CI [1.58-2.50], p < 0.001, I2 = 50.1%; OR = 2.66, 95% CI [2.02-3.15], p < 0.001; I2 = 62.5%, respectively). GERD was associated with an elevated risk of poor sleep quality (OR = 1.47, 95% CI [1.47-1.79], p < 0.001, I2 = 72.4%), sleep disturbance (OR = 1.47, 95% CI [1.24-1.74], p < 0.001, I2 = 71.6%), or short sleep duration (OR = 1.17, 95% CI [1.12-1.21], p < 0.001, I2 = 0).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis establishes a bidirectional relationship between four distinct types of sleep problems and GERD. The findings offer insights for the development of innovative approaches in the treatment of both GERD and sleep problems.
Keywords: GERD; Gastroesophageal reflux disease; Insomnia; Poor sleep quality; Short sleep duration; Sleep disturbance.
© 2024 Tan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The association between gastroesophageal reflux disease with sleep quality, depression, and anxiety in a cohort study of Australian men.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Jun;32(6):1170-1177. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13650. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 27862259
-
Alcohol Consumption and the Risk of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Alcohol Alcohol. 2019 Jan 1;54(1):62-69. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agy063. Alcohol Alcohol. 2019. PMID: 30184159
-
Relationships between sleep disturbances and gastroesophageal reflux disease in Asian sleep clinic referrals.J Psychosom Res. 2013 Dec;75(6):551-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Oct 16. J Psychosom Res. 2013. PMID: 24290045
-
Prevalence of sleep disorders among first responders for medical emergencies: A meta-analysis.J Glob Health. 2022 Oct 20;12:04092. doi: 10.7189/jogh.12.04092. J Glob Health. 2022. PMID: 36269052 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of bidirectional associations between gastroesophageal reflux disease and periodontitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Dis Esophagus. 2025 May 3;38(3):doaf031. doi: 10.1093/dote/doaf031. Dis Esophagus. 2025. PMID: 40319483
Cited by
-
The association between GERD symptoms severity and psychosocial health in palestine: a cross-sectional study.BMC Res Notes. 2025 Aug 17;18(1):357. doi: 10.1186/s13104-025-07449-z. BMC Res Notes. 2025. PMID: 40820143 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Animal Model Methods: A Data Mining of the Past Decade.Dig Dis Sci. 2025 Jul;70(7):2340-2347. doi: 10.1007/s10620-025-09022-x. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Dig Dis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40167947
References
-
- Baglioni C, Battagliese G, Feige B, Spiegelhalder K, Nissen C, Voderholzer U, Lombardo C, Riemann D. Insomnia as a predictor of depression: a meta-analytic evaluation of longitudinal epidemiological studies. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2011;135(1–3):10–19. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.01.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chang C-H, Chen T-H, Chiang L-LL, Hsu C-L, Yu H-C, Mar G-Y, Ma C-C. Associations between lifestyle habits, perceived symptoms and gastroesophageal reflux disease in patients seeking health check-ups. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021;18(7):3808. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18073808. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

