A case report and literature review on tocilizumab-cured acute necrotizing encephalopathy caused by influenza A virus
- PMID: 38646514
- PMCID: PMC11026575
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2024.1351478
A case report and literature review on tocilizumab-cured acute necrotizing encephalopathy caused by influenza A virus
Abstract
Introduction: Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy (ANE), is a kind of severe Central Nervous System Disease. The commonest pathogen is the influenza virus. The pathogenesis of ANE is bound up to genetic susceptibility and cytokine storm. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is deemed as the core function in cytokine storm of ANE and that plays a significant role in evaluating the severity of Influenza-Related ANE. Tocilizumab, an IL-6 antagonist, is known to be safe and effective in the treatment of ANE when used early and has an essential role in improving prognosis and preventing disability.
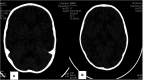
Case report: This case reports a 2 year 10 month old boy who developed ANE after being infected with influenza A virus (H1N1-2019). After treatment with Tocilizumab, the child's consciousness was clear, no convulsions occurred, the movement of limbs was improved, and the lesions of encephalopathy were significantly reduced.
Conclusion: The early use of Tocilizumab is safe and effective for the treatment of ANE caused by influenza virus.
Keywords: Tolizumab; acute necrotizing encephalopathy; children; cytokine storm; influenza A virus; interleukin-6; prognosis.
© 2024 Huang, Zhou, Hong and Cai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute necrotizing encephalopathy in adult patients with influenza: a case report and review of the literature.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 9;24(1):931. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09844-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39251995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine Storm Related to CD4+ T Cells in Influenza Virus-Associated Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy.Immune Netw. 2024 Apr 29;24(2):e18. doi: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e18. eCollection 2024 Apr. Immune Netw. 2024. PMID: 38725671 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of severe acute necrotizing encephalopathy of childhood with interleukin-6 receptor blockade in the first 24 h as add-on immunotherapy shows favorable long-term outcome at 2 years.Brain Dev. 2023 Aug;45(7):401-407. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2023.03.002. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Brain Dev. 2023. PMID: 36967317
-
Early therapeutic plasma exchange may lead to complete neurological recovery in moderate to severe influenza-associated acute necrotizing encephalopathy.Brain Dev. 2022 Aug;44(7):492-497. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2022.03.004. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Brain Dev. 2022. PMID: 35337691
-
Pathogenesis and Management of Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy.Expert Rev Neurother. 2023 Jul-Dec;23(7):641-650. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2023.2224503. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Expert Rev Neurother. 2023. PMID: 37309119 Review.
Cited by
-
Highly beneficial outcome in severe acute necrotizing encephalopathy with tocilizumab treatment.J Neurol. 2024 Oct;271(10):7042-7045. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12661-1. Epub 2024 Sep 6. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39242371 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Acute necrotizing encephalopathy in adult patients with influenza: a case report and review of the literature.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 9;24(1):931. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09844-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39251995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen JH, Zheng YJ, He YX, Shen KL. Reserch progress of respiratory virus infection associated acute necrotizing encephalopathy. Chin J Appl Clin Pediatr. (2023) 01:10–6. 10.3760/cma.j.cn101070-20230106-00008 - DOI
-
- Wang YQ, Qian SY, Li KC, Xie ZD. Epidemiological characteristics and prognosis of acute necrotizing encephalopathy in children. Chin Pediatr Emerg Med. (2021) 10:910–3. 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4912.2021.10.014 - DOI
-
- Grohskopf LA, Alyanak E, Broder KR, Chung JR, Broder KR, Talbot HK, et al. Prevention and control of seasonal influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the advisory committee on immunization practices—united States, 2019–20 influenza season. MMWR Recomm Rep. (2019) 68:1–21. 10.15585/mmwr.rr6803a1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources