Efficacy and safety of different systemic drugs in the treatment of uremic pruritus among hemodialysis patients: a network meta-analysis based on randomized clinical trials
- PMID: 38646551
- PMCID: PMC11026555
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1334944
Efficacy and safety of different systemic drugs in the treatment of uremic pruritus among hemodialysis patients: a network meta-analysis based on randomized clinical trials
Abstract
Aim: This network meta-analysis was to analyze and rank the efficacy and safety of different systemic drugs in the treatment of uremic pruritus (UP) among hemodialysis patients.
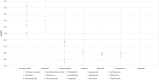
Method: PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were searched from inception to 10 July 2023 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating different drugs in the treatment of UP among hemodialysis patients. Drugs including cromolyn sodium, dexchlorpheniramine, difelikefalin, gabapentin, hydroxyzine, ketotifen, melatonin, montelukast, nalbuphine, nalfurafine, nemolizumab, nicotinamide, pregabalin, sertraline, thalidomide, and placebo were assessed. Outcome measures, including pruritus relief, response, and adverse events, were analyzed. Network plots, forest plots, league tables, and the surface under the cumulative ranking (SUCRA) probabilities were depicted for each outcome.
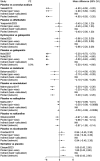
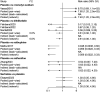
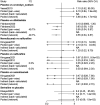
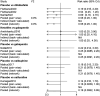
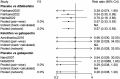
Results: The network meta-analysis retrieved 22 RCTs. Gabapentin (69.74%) had the highest likelihood to be the most effective drug for pruritus relief in UP patients receiving hemodialysis, followed by cromolyn sodium and hydroxyzine. Thalidomide (60.69%) and gabapentin (58.99%) were associated with significantly more drug responses for treating UP among patients receiving hemodialysis. Patients who were treated with gabapentin (40.01%) were likely to have risks of adverse events and dizziness. Lower risks of adverse events, nausea, and diarrhea were found in patients who received cromolyn sodium and lower risks of somnolence.
Conclusion: This study suggests considering gabapentin treatment when facing a patient suffering from UP. This study provides a reference for the selection of drug therapy for UP patients receiving hemodialysis.
Keywords: Bayesian; hemodialysis; network meta-analysis; systemic drugs; uremic pruritus.
Copyright © 2024 Zhao, Sun and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of Gabapentin and Ketotifen in Treatment of Uremic Pruritus in Hemodialysis Patients.Pak J Med Sci. 2016 Jan-Feb;32(1):22-6. doi: 10.12669/pjms.321.8547. Pak J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27022338 Free PMC article.
-
Difelikefalin in the treatment of hemodialysis patients with pruritus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 6;15:1476587. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1476587. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39712488 Free PMC article.
-
Gabapentin for uremic pruritus: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Int J Dermatol. 2020 Apr;59(4):412-422. doi: 10.1111/ijd.14708. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Int J Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31777066
-
Efficacy and Safety of Pregabalin and Gabapentin for Pruritus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Pain Symptom Manage. 2025 Jan;69(1):65-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2024.08.028. Epub 2024 Aug 21. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2025. PMID: 39173895
-
Gabapentin for uremic pruritus in hemodialysis patients: a qualitative systematic review.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2016 Mar 28;3:14. doi: 10.1186/s40697-016-0107-8. eCollection 2016. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27022475 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Management of CKD-Associated Pruritus: Current Insights.Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2024 Dec 28;17:339-354. doi: 10.2147/IJNRD.S499798. eCollection 2024. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 39748827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pruritus in Uremic Patients: Approaches to Alleviating a Common Symptom in Chronic Kidney Disease.Life (Basel). 2025 Jun 24;15(7):1001. doi: 10.3390/life15071001. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40724504 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Daraghmeh M, Badran M, Janajreh A, Hassan M, Taha AA, Koni AA, et al. . Prevalence of pruritus associated with hemodialysis and its association with sleep quality among hemodialysis patients: a multicenter study. BMC Nephrol. (2022) 23:213. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-02838-z, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

