IL4 receptor targeting enables nab-paclitaxel to enhance reprogramming of M2-type macrophages into M1-like phenotype via ROS-HMGB1-TLR4 axis and inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis
- PMID: 38646639
- PMCID: PMC11024855
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.92672
IL4 receptor targeting enables nab-paclitaxel to enhance reprogramming of M2-type macrophages into M1-like phenotype via ROS-HMGB1-TLR4 axis and inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis
Abstract
Rationale: Nab-paclitaxel (Abx) is widely employed in malignant tumor therapy. In tumor cells and pro-tumoral M2-type macrophages, the IL4 receptor (IL4R) is upregulated. This study aimed to elucidate the selective delivery of Abx to M2-type macrophages by targeting IL4R and reprogramming them into an anti-tumoral M1-type. Methods: Abx was conjugated with the IL4R-binding IL4RPep-1 peptide using click chemistry (IL4R-Abx). Cellular internalization, macrophage reprogramming and signal pathways, and tumor growth and metastasis by IL4R-Abx were examined. Results: IL4R-Abx was internalized into M2 macrophages more efficiently compared to the unmodified Abx and control peptide-conjugated Abx (Ctrl-Abx), which was primarily inhibited using an anti-IL4R antibody and a receptor-mediated endocytosis inhibitor compared with a macropinocytosis inhibitor. IL4R-Abx reprogrammed the M2-type macrophages into M1-like phenotype and increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and extracellular release of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in M2 macrophages at higher levels than Abx and Ctrl-Abx. The conditioned medium of IL4R-Abx-treated M2 macrophages skewed M2 macrophages into the M1-like phenotype, in which an anti-HMGB1 antibody and a toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) inhibitor induced a blockade. IL4R-Abx accumulated at tumors, heightened immune-stimulatory cells while reducing immune-suppressing cells, and hampered tumor growth and metastasis in mice more efficiently than Abx and Ctrl-Abx. Conclusions: These results indicate that IL4R-targeting allows enhancement of M2-macrophage shaping into M1-like phenotype by Abx through the ROS-HMGB1-TLR4 axis, improvement of antitumor immunity, and thereby inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis, presenting a new approach to cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: IL4 receptor; M2-macrophage; immunotherapy; nab-paclitaxel; reprogramming.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


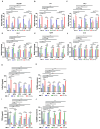
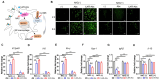
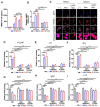
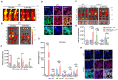
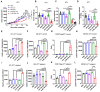
 M2 macrophages (F), CD8/Treg ratio (G), and CD45+F4/80-Ly6C+CD11b+ MDSCs (H) in 0.1 g of tumor tissues and the population of M1 macrophages (I), M2 macrophages (J), CD8/Treg ratio (K), and MDSCs (L) in 105 cells of spleen were determined. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. P values compared to saline-treated group are shown on the top of bars. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple post hoc test. (A, n = 10 per group; B-D, n = 6 per group; E-L, n = 4 per group).
M2 macrophages (F), CD8/Treg ratio (G), and CD45+F4/80-Ly6C+CD11b+ MDSCs (H) in 0.1 g of tumor tissues and the population of M1 macrophages (I), M2 macrophages (J), CD8/Treg ratio (K), and MDSCs (L) in 105 cells of spleen were determined. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. P values compared to saline-treated group are shown on the top of bars. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple post hoc test. (A, n = 10 per group; B-D, n = 6 per group; E-L, n = 4 per group).
References
-
- Mantovani A, Sica A. Macrophages, innate immunity and cancer: balance, tolerance, and diversity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2010;22:231–7. - PubMed
-
- Aapro MS, Von Minckwitz G. Molecular basis for the development of novel taxanes in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Eur J Cancer Suppl. 2008;6:3–11.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

