Regulation of CNS pathology by Serpina3n/SERPINA3: The knowns and the puzzles
- PMID: 38647003
- PMCID: PMC11131959
- DOI: 10.1111/nan.12980
Regulation of CNS pathology by Serpina3n/SERPINA3: The knowns and the puzzles
Abstract
Neuroinflammation, blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction, neuron and glia injury/death and myelin damage are common central nervous system (CNS) pathologies observed in various neurological diseases and injuries. Serine protease inhibitor (Serpin) clade A member 3n (Serpina3n), and its human orthologue SERPINA3, is an acute-phase inflammatory glycoprotein secreted primarily by the liver into the bloodstream in response to systemic inflammation. Clinically, SERPINA3 is dysregulated in brain cells, cerebrospinal fluid and plasma in various neurological conditions. Although it has been widely accepted that Serpina3n/SERPINA3 is a reliable biomarker of reactive astrocytes in diseased CNS, recent data have challenged this well-cited concept, suggesting instead that oligodendrocytes and neurons are the primary sources of Serpina3n/SERPINA3. The debate continues regarding whether Serpina3n/SERPINA3 induction represents a pathogenic or a protective mechanism. Here, we propose possible interpretations for previously controversial data and present perspectives regarding the potential role of Serpina3n/SERPINA3 in CNS pathologies, including demyelinating disorders where oligodendrocytes are the primary targets. We hypothesise that the 'good' or 'bad' aspects of Serpina3n/SERPINA3 depend on its cellular sources, its subcellular distribution (or mis-localisation) and/or disease/injury types. Furthermore, circulating Serpina3n/SERPINA3 may cross the BBB to impact CNS pathologies. Cell-specific genetic tools are critically important to tease out the potential roles of cell type-dependent Serpina3n in CNS diseases/injuries.
Keywords: Serpina3n/SERPINA3; blood–brain barrier; cell death/survival; multiple sclerosis; myelin; neuroinflammation; neurological disease/injury; neuron/glia.
© 2024 British Neuropathological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
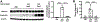
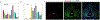
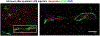
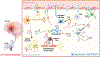
References
-
- Gatto M, Iaccarino L, Ghirardello A, Bassi N, Pontisso P, Punzi L, Shoenfeld Y, Doria A, Serpins, immunity and autoimmunity: old molecules, new functions, Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 45(2) (2013) 267–80. - PubMed
-
- Abraham CR, Selkoe DJ, Potter H, Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease, Cell 52(4) (1988) 487–501. - PubMed
-
- Abraham CR, Potter H, The protease inhibitor, alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, is a component of the brain amyloid deposits in normal aging and Alzheimer's disease, Ann Med 21(2) (1989) 77–81. - PubMed
-
- DeKosky ST, Ikonomovic MD, Wang X, Farlow M, Wisniewski S, Lopez OL, Becker JT, Saxton J, Klunk WE, Sweet R, Kaufer DI, Kamboh MI, Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid alpha1-antichymotrypsin levels in Alzheimer's disease: correlation with cognitive impairment, Ann Neurol 53(1) (2003) 81–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

