Home-Based Cognitive Intervention for Healthy Older Adults Through Asking Robots Questions: Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 38647260
- PMCID: PMC11058555
- DOI: 10.2196/47229
Home-Based Cognitive Intervention for Healthy Older Adults Through Asking Robots Questions: Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Asking questions is common in conversations, and while asking questions, we need to listen carefully to what others say and consider the perspective our questions adopt. However, difficulties persist in verifying the effect of asking questions on older adults' cognitive function due to the lack of a standardized system for conducting experiments at participants' homes.
Objective: This study examined the intervention effect of cognitive training moderated by robots on healthy older adults. A focus on the feasibility of the intervention at participants' homes was also maintained. Feasibility was evaluated by considering both the dropout rate during the intervention and the number of questions posed to each participant during the experiment.
Methods: We conducted a randomized controlled trial with 81 adults older than 65 years. Participants were recruited through postal invitations and then randomized into 2 groups. The intervention group (n=40) received sessions where participants listened to photo-integrated stories and posed questions to the robots. The control group (n=41) received sessions where participants listened to photo-integrated stories and only thanked the robots for confirming participation. The participants participated in 12 dialogue sessions for 2-3 weeks. Scores of global cognitive functioning tests, recall tests, and verbal fluency tasks measured before and after the intervention were compared between the 2 groups.
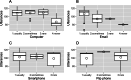
Results: There was no significant intervention effect on the Telephone Interview for Cognitive Status-Japanese scores, recall tests, and verbal fluency tasks. Additionally, our study successfully concluded with no participant dropouts at follow-up, confirming the feasibility of our approach.
Conclusions: There was no statistically significant evidence indicating intervention benefits for cognitive functioning. Although the feasibility of home-based interventions was demonstrated, we identified areas for improvement in the future, such as setting up more efficient session themes. Further research is required to identify the effectiveness of an improved cognitive intervention involving the act of asking questions.
Keywords: cognitive intervention; digital health; home-based experiment; older adults; robots; technology adoption.
© Seiki Tokunaga, Takuya Sekiguchi, Kumi Watanabe Miura, Hikaru Sugimoto, Masato S Abe, Kazuhiro Tamura, Taishiro Kishimoto, Takashi Kudo, Mihoko Otake-Matsuura. Originally published in JMIR Aging (https://aging.jmir.org).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Online Group-Based Dual-Task Training to Improve Cognitive Function of Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Randomized Controlled Feasibility Study.JMIR Aging. 2025 May 16;8:e67267. doi: 10.2196/67267. JMIR Aging. 2025. PMID: 40378407 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cognitive Intervention Through Photo-Integrated Conversation Moderated by Robots (PICMOR) Program: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Front Robot AI. 2021 Apr 12;8:633076. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2021.633076. eCollection 2021. Front Robot AI. 2021. PMID: 33969003 Free PMC article.
-
A Dialogue-Based System with Photo and Storytelling for Older Adults: Toward Daily Cognitive Training.Front Robot AI. 2021 Jun 29;8:644964. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2021.644964. eCollection 2021. Front Robot AI. 2021. PMID: 34268339 Free PMC article.
-
Computerised cognitive training for 12 or more weeks for maintaining cognitive function in cognitively healthy people in late life.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Feb 27;2(2):CD012277. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012277.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32104914 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

