Statistical Genomics Analysis of Simple Sequence Repeats from the Paphiopedilum Malipoense Transcriptome Reveals Control Knob Motifs Modulating Gene Expression
- PMID: 38647414
- PMCID: PMC11200097
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202304848
Statistical Genomics Analysis of Simple Sequence Repeats from the Paphiopedilum Malipoense Transcriptome Reveals Control Knob Motifs Modulating Gene Expression
Abstract
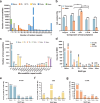
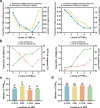
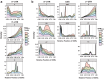
Simple sequence repeats (SSRs) are found in nonrandom distributions in genomes and are thought to impact gene expression. The distribution patterns of 48 295 SSRs of Paphiopedilum malipoense are mined and characterized based on the first full-length transcriptome and comprehensive transcriptome dataset from 12 organs. Statistical genomics analyses are used to investigate how SSRs in transcripts affect gene expression. The results demonstrate the correlations between SSR distributions, characteristics, and expression level. Nine expression-modulating motifs (expMotifs) are identified and a model is proposed to explain the effect of their key features, potency, and gene function on an intra-transcribed region scale. The expMotif-transcribed region combination is the most predominant contributor to the expression-modulating effect of SSRs, and some intra-transcribed regions are critical for this effect. Genes containing the same type of expMotif-SSR elements in the same transcribed region are likely linked in function, regulation, or evolution aspects. This study offers novel evidence to understand how SSRs regulate gene expression and provides potential regulatory elements for plant genetic engineering.
Keywords: Paphiopedilum malipoense; full‐length transcriptomes; gene expression; motif types; simple sequence repeats (SSRs).
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development and characterization of genomic and expressed SSRs in citrus by genome-wide analysis.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 28;8(10):e75149. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075149. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24204572 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and conservation of simple sequence repeats in plant pathogenic species of Zymoseptoria and development of genomic resources for its orphaned species.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2024 Jan 3;117(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s10482-023-01915-z. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2024. PMID: 38170404
-
ChloroSSRdb: a repository of perfect and imperfect chloroplastic simple sequence repeats (cpSSRs) of green plants.Database (Oxford). 2014 Nov 7;2014:bau107. doi: 10.1093/database/bau107. Print 2014. Database (Oxford). 2014. PMID: 25380781 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of genic-SSR markers in sesame by RNA-seq.BMC Genomics. 2012 Jul 16;13:316. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-316. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22800194 Free PMC article.
-
Microsatellites within genes: structure, function, and evolution.Mol Biol Evol. 2004 Jun;21(6):991-1007. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh073. Epub 2004 Feb 12. Mol Biol Evol. 2004. PMID: 14963101 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinal Variation in Short Tandem Repeats Linked to Gene Expression in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.).Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 3;14(8):944. doi: 10.3390/biom14080944. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199332 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying associations between short tandem repeat sequences and gene expression in yeast reveals specific repeated motifs encoding transcriptional regulatory proteins.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 Feb 14;27:705-716. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.02.003. eCollection 2025. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40092660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Erwin G. S., Gürsoy G., Al‐Abri R., Suriyaprakash A., Dolzhenko E., Zhu K., Hoerner C. R., White S. M., Ramirez L., Vadlakonda A., Vadlakonda A., Von Kraut K., Park J., Brannon C. M., Sumano D. A., Kirtikar R. A., Erwin A. A., Metzner T. J., Yuen R. K. C., Fan A. C., Leppert J. T., Eberle M. A., Gerstein M., Snyder M. P., Nature 2023, 613, 96. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 31872670/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32071781/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021A1515010911/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- 202206010107/Science and Technology Projects in Guangzhou
- JCYJ20190813172001780/Department of Science and Technology of Shenzhen City
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
