Effects of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles on sulfate bioreduction and oxidative stress in Desulfovibrio desulfuricans
- PMID: 38647594
- PMCID: PMC10991916
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-022-00523-5
Effects of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles on sulfate bioreduction and oxidative stress in Desulfovibrio desulfuricans
Abstract
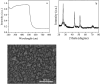
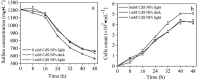
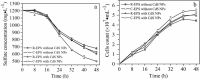
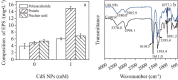
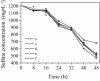
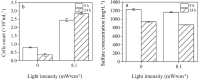
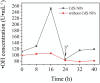
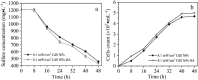
Sulfate-containing wastewater has a serious threat to the environment and human health. Microbial technology has great potential for the treatment of sulfate-containing wastewater. It was found that nano-photocatalysts could be used as extracellular electron donors to promote the growth and metabolic activity of non-photosynthetic microorganisms. However, nano-photocatalysts could also induce oxidative stress and damage cells. Therefore, the interaction mechanism between photosynthetic nanocatalysts and non-photosynthetic microorganisms is crucial to determine the regulatory strategies for microbial wastewater treatment technologies. In this paper, the mechanism and regulation strategy of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles (CdS NPs) on the growth of sulfate-reducing bacteria and the sulfate reduction process were investigated. The results showed that the sulfate reduction efficiency could be increased by 6.4% through CdS NPs under light conditions. However, the growth of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans C09 was seriously inhibited by 55% due to the oxidative stress induced by CdS NPs on cells. The biomass and sulfate reduction efficiency could be enhanced by 6.8% and 5.9%, respectively, through external addition of humic acid (HA). At the same time, the mechanism of the CdS NPs strengthening the sulfate reduction process by sulfate bacteria was also studied which can provide important theoretical guidance and technical support for the development of microbial technology combined with extracellular electron transfer (EET) for the treatment of sulfate-containing wastewater.
Keywords: Desulfovibrio desulfuricans; Cadmium sulfide nanoparticles; Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS); Oxidative stress; Sulfate reduction.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Sulfate Reduction and Cell Division by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans Coated in Palladium Metal.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Jun 28;88(12):e0058022. doi: 10.1128/aem.00580-22. Epub 2022 May 31. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35638843 Free PMC article.
-
Factors affecting microbial sulfate reduction by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans in continuous culture: limiting nutrients and sulfide concentration.Biotechnol Bioeng. 1992 Sep;40(6):725-34. doi: 10.1002/bit.260400612. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1992. PMID: 18601173
-
Cadmium sulfide nanoparticles-assisted intimate coupling of microbial and photoelectrochemical processes: Mechanisms and environmental applications.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Oct 20;740:140080. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140080. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 32562993 Review.
-
Mediated biosynthesis of CdS QDs by EPS from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans sub sp. under carbon source-induced reinforcement.J Hazard Mater. 2023 Oct 5;459:132146. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132146. Epub 2023 Jul 24. J Hazard Mater. 2023. PMID: 37499495
-
Recent advances in dissimilatory sulfate reduction: From metabolic study to application.Water Res. 2019 Mar 1;150:162-181. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.11.018. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Water Res. 2019. PMID: 30508713 Review.
Cited by
-
The Influence of Exogenous CdS Nanoparticles on the Growth and Carbon Assimilation Efficiency of Escherichia coli.Biology (Basel). 2024 Oct 21;13(10):847. doi: 10.3390/biology13100847. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452155 Free PMC article.
-
Cadmium effects on net N2O production by the deep-sea isolate Shewanella loihica PV-4.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2023 Jan 17;370:fnad047. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnad047. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37279908 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of Growth Conditions of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans Strain REO-01 and Evaluation of Its Cd(II) Bioremediation Potential for Detoxification of Rare Earth Tailings.Microorganisms. 2025 Jun 28;13(7):1511. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13071511. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40732020 Free PMC article.
-
Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications.Molecules. 2023 May 2;28(9):3857. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093857. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175267 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cao B, Shi L, Brown RN, Xiong Y, Fredrickson JK, Romine MF, Marshall MJ, Lipton MS, Beyenal H. Extracellular polymeric substances from Shewanella sp. HRCR-1 biofilms: characterization by infrared spectroscopy and proteomics. Environ Microbiol. 2011;13:1018–1031. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02407.x. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

