Hearing Difficulties Among Farmworkers in the México-US Southwest Border Region
- PMID: 38647631
- PMCID: PMC11289265
- DOI: 10.1007/s10903-024-01592-8
Hearing Difficulties Among Farmworkers in the México-US Southwest Border Region
Abstract
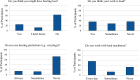
Migrant and seasonal farmworkers are a vulnerable population with a potentially high risk for hearing loss due to farm-related noise exposures. Occupational noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is permanent, and it is associated with an increased risk for injuries on the job, as well as communication difficulties, isolation, and depression. The México/US border region is one of the most productive agricultural regions in the country, however, no known studies have explored hearing loss among farmworkers in this area. This pilot study was a first step toward measuring and addressing hearing loss and noise exposure among this region's farmworkers. We conducted a cross-sectional survey to estimate the prevalence of subjective hearing difficulties among Yuma County, Arizona farmworkers. Survey interviews took place during a late-night farmworker health fair from 2 am to 6 am to accommodate local farms' labor schedules. Multivariable regression adjusted for demographic and work covariates estimated subjective hearing loss prevalence ratios. Among 132 farmworker participants, 36% reported they have or might have hearing loss, and 62% reported no hearing loss. Subjective hearing loss prevalence was lower in farmworkers who report not working in noise compared to prevalence in farmworkers who work in noise [prevalence ratio, 0.44 (95% CI 0.23-0.82)]. This report contributes to understanding the perception of hearing-related health and occupational exposures among farmworkers in the México-US Southwest border region. The information from this line of research will inform appropriate safety measures known to lower the risk of experiencing occupational NIHL.
Keywords: Exposure assessment; Farmer; Hearing loss prevention; Hearing protection; Noise; Occupational health.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noise-induced hearing loss in farmworkers: a scoping review.Front Public Health. 2025 Mar 3;13:1502489. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1502489. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40098797 Free PMC article.
-
"We All Have a Job to Do in This World, It's up to Us": Farmworker and Farmer Mental Health in a Rural US-Mexico Border Region.J Agromedicine. 2023 Jul;28(3):365-377. doi: 10.1080/1059924X.2022.2154298. Epub 2022 Dec 16. J Agromedicine. 2023. PMID: 36525583 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of early-stage hearing loss among a cohort of young workers with 16-year follow-up.Occup Environ Med. 2012 Jul;69(7):479-84. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2011-100464. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Occup Environ Med. 2012. PMID: 22447644 Clinical Trial.
-
Migrant Farmworkers' Exposure to Pesticides in Sonora, Mexico.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Nov 26;15(12):2651. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15122651. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30486281 Free PMC article.
-
Occupational hearing loss in Korea.J Korean Med Sci. 2010 Dec;25(Suppl):S62-9. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.S.S62. Epub 2010 Dec 15. J Korean Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 21258593 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Noise-induced hearing loss in farmworkers: a scoping review.Front Public Health. 2025 Mar 3;13:1502489. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1502489. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40098797 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources