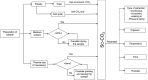
Sc-CO2 extraction of fish and fish by-products in the production of fish oil and enzyme
- PMID: 38647764
- PMCID: PMC10992331
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-022-00509-3
Sc-CO2 extraction of fish and fish by-products in the production of fish oil and enzyme
Abstract
Supercritical carbon dioxide (Sc-CO2) is an alternative tool to extract lipid for the production of fish oil and enzyme from fish by-products (FBPs). In the application of Sc-CO2, this review covers sample preparation, lipid extraction operation, and characterization of fish oil and enzyme as final products. Generally, the fish samples with moisture content less than 20% and particle size less than 5 mm are considered before lipid extraction with Sc-CO2. Sc-CO2 parameters, such as pressure (P), temperature (T), extraction time (text), and flow rate (F), for simultaneous recovery of fish oil, protein, and enzyme were found to be less severe (P: 10.3-25 MPa; T: 25-45 °C, text: 20-150 min; F: 3-50 g/min) than the extraction of fish oil alone (P: 10-40 Mpa; T: 35-80 °C; text: 30-360 min; F: 1-3000 g/min). The enzyme from the Sc-CO2 defatted sample showed higher activity up to 45 U/mg due to lower denaturation of protein as compared to the organic solvent treated sample albeit both samples having similar pH (6-10) and temperature stability (20-60 °C). Overall, mild extraction of lipid from FBPs using Sc-CO2 is effective for the production of enzymes suitable in various industrial applications. Also, fish oil as a result of extraction can be produced as a health product with high polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and low contamination of heavy metals.
Keywords: Defatted; Digestive enzymes; Fish by-products; Fish oil; Protein; Sc-CO2.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of digestive enzymes from de-oiled mackerel (Scomber japonicus) muscle obtained by supercritical carbon dioxide and n-hexane extraction as a comparative study.J Food Sci Technol. 2015 Jun;52(6):3494-503. doi: 10.1007/s13197-014-1408-5. Epub 2014 May 24. J Food Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 26028731 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of the quality characteristics of defatted soy flour treated by supercritical carbon dioxide and organic solvent.J Food Sci Technol. 2017 Jul;54(8):2485-2493. doi: 10.1007/s13197-017-2691-8. Epub 2017 May 29. J Food Sci Technol. 2017. PMID: 28740306 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the impact of supercritical-CO2 pressure on the recovery and quality of oil from "horchata" by-products: Fatty acid profile, α-tocopherol, phenolic compounds, and lipid oxidation parameters.Food Res Int. 2019 Jun;120:888-894. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.11.054. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Food Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31000310
-
Supercritical extraction of sunflower oil: A central composite design for extraction variables.Food Chem. 2016 Feb 1;192:647-59. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.070. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 26304395
-
Supercritical CO2 Extraction of Rice Bran Oil -the Technology, Manufacture, and Applications.J Oleo Sci. 2017 Jun 1;66(6):557-564. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess17019. Epub 2017 May 17. J Oleo Sci. 2017. PMID: 28515385 Review.
Cited by
-
Nutraceutical and Medicinal Importance of Marine Molluscs.Mar Drugs. 2024 Apr 27;22(5):201. doi: 10.3390/md22050201. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38786591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abe K, Yuan C, Kumagai Y, Kishimura H. The potential of freshwater fish viscus from silver carp hypophthalmichthys molitrix for trypsin source. Waste Biomass Valorization. 2020;11:3971–3978. doi: 10.1007/s12649-019-00717-7. - DOI
-
- Adeoti IA, Hawboldt K. A review of lipid extraction from fish processing by-product for use as a biofuel. Biomass Bioenerg. 2014;63:330–340. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2014.02.011. - DOI
-
- Ahmed R, Haq M, Cho YJ, Chun BS. Quality evaluation of oil recovered from by-products of bigeye tuna using supercritical carbon dioxide extraction. Turkish J Fish Aquat Sci. 2017;17:663–672. doi: 10.4194/1303-2712-v17_4_02. - DOI
-
- Ali-Nehari A, Kim SB, Lee YB, Chun BS. Digestive enzymes characterization of krill (Euphausia superba) residues deoiled by supercritical carbon dioxide and organic solvents. J Ind Eng Chem. 2012;18:1314–1319. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2012.01.026. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources