Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses provide insights into the adaptive responses to the combined impact of salinity and alkalinity in Gymnocypris przewalskii
- PMID: 38647776
- PMCID: PMC10992934
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-022-00589-1
Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses provide insights into the adaptive responses to the combined impact of salinity and alkalinity in Gymnocypris przewalskii
Abstract
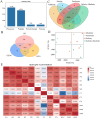
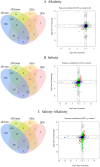
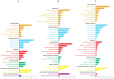
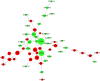
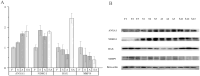
Gymnocypris przewalskii is the only high-land endemic teleost living in Qinghai Lake, the largest saline-alkaline lake in China. Its osmoregulatory physiology remains elusive due to a lack of precise identification of the response proteins. In the present study, DIA/SWATH was used to identify differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) under alkaline (pH = 10.1, carbonate buffer), saline (12‰, sodium chloride), and saline-alkaline [carbonate buffer (pH = 10.1) plus 11‰ sodium chloride] stresses. A total of 66,056 unique peptides representing 7,150 proteins and 230 DEPs [the false discovery rate (FDR) ≤ 0.05, fold change (FC) ≥ 1.5] were identified under different stresses. Comparative analyses of the proteome and transcriptome indicated that over 86% of DEPs did not show consistent trends with mRNA. In addition to consistent enrichment results under different stresses, the specific DEPs involved in saline-alkaline adaptation were primarily enriched in functions of homeostasis, hormone synthesis and reactions of defense response, complement activation and reproductive development. Meanwhile, a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis of these specific DEPs indicated that the hub genes were ITGAX, MMP9, C3, F2, CD74, BTK, ANXA1, NCKAP1L, and CASP8. This study accurately isolated the genes that respond to stress, and the results could be helpful for understanding the physiological regulation mechanisms regarding salinity, alkalinity, and salinity-alkalinity interactions.
Keywords: Gymnocypris przewalskii; Alkalinity; DIA/SWATH; Salinity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Royal Statistical Society Series b: Methodol. 1995;57(1):289–300.
-
- Betts J, et al. Anatomy and Physiology. Houston: Rice University; 2013.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

