Toward improved terpenoids biosynthesis: strategies to enhance the capabilities of cell factories
- PMID: 38647812
- PMCID: PMC10992668
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-022-00493-8
Toward improved terpenoids biosynthesis: strategies to enhance the capabilities of cell factories
Abstract
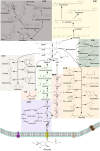
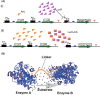
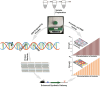
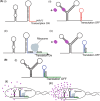
Terpenoids form the most diversified class of natural products, which have gained application in the pharmaceutical, food, transportation, and fine and bulk chemical industries. Extraction from naturally occurring sources does not meet industrial demands, whereas chemical synthesis is often associated with poor enantio-selectivity, harsh working conditions, and environmental pollutions. Microbial cell factories come as a suitable replacement. However, designing efficient microbial platforms for isoprenoid synthesis is often a challenging task. This has to do with the cytotoxic effects of pathway intermediates and some end products, instability of expressed pathways, as well as high enzyme promiscuity. Also, the low enzymatic activity of some terpene synthases and prenyltransferases, and the lack of an efficient throughput system to screen improved high-performing strains are bottlenecks in strain development. Metabolic engineering and synthetic biology seek to overcome these issues through the provision of effective synthetic tools. This review sought to provide an in-depth description of novel strategies for improving cell factory performance. We focused on improving transcriptional and translational efficiencies through static and dynamic regulatory elements, enzyme engineering and high-throughput screening strategies, cellular function enhancement through chromosomal integration, metabolite tolerance, and modularization of pathways.
Keywords: Cellular tolerance; Chromosomal integration; Dynamic regulation; Modular engineering; Promoter engineering; Protein engineering; RBS engineering; Terpenoids.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors consent to publishing the manuscript in
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed MS, Ikram S, Rasool A, Li C. Design and construction of short synthetic terminators for β-amyrin production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Eng J. 2019;146:105–116. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2019.03.011. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

