Engineering growth phenotypes of Aspergillus oryzae for L-malate production
- PMID: 38647943
- PMCID: PMC10991988
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-023-00642-7
Engineering growth phenotypes of Aspergillus oryzae for L-malate production
Abstract
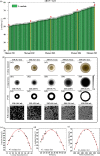
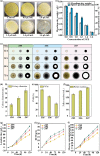
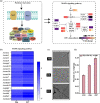
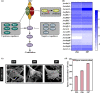
Improving the growth status of Aspergillus oryzae is an efficient way to enhance L-malate production. However, the growth mechanism of filamentous fungi is relatively complex, which limits A. oryzae as a cell factory to produce L-malate industrially. This study determined the relationship between growth status and L-malate production. The optimal ranges of colony diameter, percentage of vegetative mycelia, and pellet number of A. oryzae were determined to be 26-30 mm, 35-40%, and 220-240/mL, respectively. To achieve this optimum range, adaptive evolution was used to obtain the evolved strain Z07 with 132.54 g/L L-malate and a productivity of 1.1 g/L/h. Finally, a combination of transcriptome analysis and morphological characterization was used to identify the relevant pathway genes that affect the growth mechanism of A. oryzae. The strategies used in this study and the growth mechanism provide a good basis for efficient L-malate production by filamentous fungi.
Keywords: Aspergillus oryzae; Adaptive evolution; Growth mechanism; Growth phenotypes; L-malate.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Brown SH, Bashkirova L, Berka R, Chandler T, Doty T, McCall K, McCulloch M, McFarland S, Thompson S, Yaver D, Berry A. Metabolic engineering of Aspergillus oryzae NRRL 3488 for increased production of L-malic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;97(20):8903–8912. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5132-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Crescenzi O, Kurtz M, Champe S. Developmental defects resulting from arginine auxotrophy in Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1983;129:3535–3544. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 32021005/the Science Fund for Creative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 22038005/the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20211529/the Provincial Outstanding Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- JUSRP22031/the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

