Characterization of cold-active trehalose synthase from Pseudarthrobacter sp. for trehalose bioproduction
- PMID: 38647947
- PMCID: PMC10992939
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-023-00681-0
Characterization of cold-active trehalose synthase from Pseudarthrobacter sp. for trehalose bioproduction
Abstract
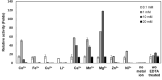
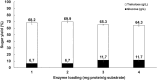
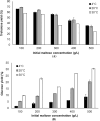
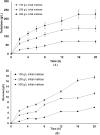
Trehalose is a functional sugar that has numerous applications in food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical products. Production of trehalose from maltose via a single-step enzymatic catalysis using trehalose synthase (TreS) is a promising method compared with the conventional two-step process due to its simplicity with lower formation of byproducts. In this study, a cold-active trehalose synthase (PaTreS) from Pseudarthrobacter sp. TBRC 2005 was heterologously expressed and characterized. PaTreS showed the maximum activity at 20 °C and maintained 87% and 59% of its activity at 10 °C and 4 °C, respectively. The enzyme had remarkable stability over a board pH range of 7.0-9.0 with the highest activity at pH 7.0. The activity was enhanced by divalent metal ions (Mg2+, Mn2+ and Ca2+). Conversion of high-concentration maltose syrup (100-300 g/L) using PaTreS yielded 71.7-225.5 g/L trehalose, with 4.5-16.4 g/L glucose as a byproduct within 16 h. The work demonstrated the potential of PaTreS as a promising biocatalyst for the development of low-temperature trehalose production, with the advantages of reduced risk of microbial contamination with low generation of byproduct.
Keywords: Pseudarthrobacter sp; Cold active enzyme; Maltose; Trehalose; Trehalose synthase.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Burek M, Waśkiewicz S, Wandzik I, Kamińska K. Trehalose—properties, biosynthesis and applications. Chemik. 2015;69(8):469–476.
-
- Cai X, Seitl I, Mu W, Zhang T, Stressler T, Fischer L, Jiang B. Characterization of a recombinant trehalose synthase from arthrobacter chlorophenolicus and its unique kinetics indicating a substrate cooperativity. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019;187(4):1255–1271. doi: 10.1007/s12010-018-2877-1. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

