Membrane-bound O-acyltransferase 7 (MBOAT7) shapes lysosomal lipid homeostasis and function to control alcohol-associated liver injury
- PMID: 38648183
- PMCID: PMC11034944
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.92243
Membrane-bound O-acyltransferase 7 (MBOAT7) shapes lysosomal lipid homeostasis and function to control alcohol-associated liver injury
Abstract
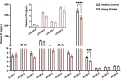
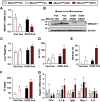
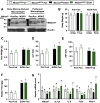
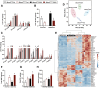
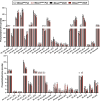
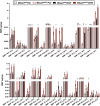
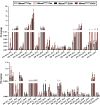
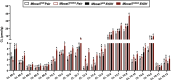
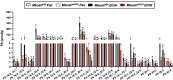
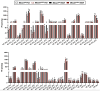
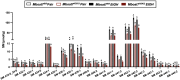
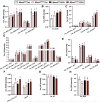
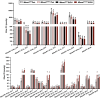
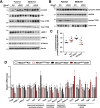
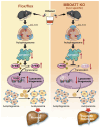
Recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified a link between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) near the MBOAT7 gene and advanced liver diseases. Specifically, the common MBOAT7 variant (rs641738) associated with reduced MBOAT7 expression is implicated in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD), and liver fibrosis. However, the precise mechanism underlying MBOAT7-driven liver disease progression remains elusive. Previously, we identified MBOAT7-driven acylation of lysophosphatidylinositol lipids as key mechanism suppressing the progression of NAFLD (Gwag et al., 2019). Here, we show that MBOAT7 loss of function promotes ALD via reorganization of lysosomal lipid homeostasis. Circulating levels of MBOAT7 metabolic products are significantly reduced in heavy drinkers compared to healthy controls. Hepatocyte- (Mboat7-HSKO), but not myeloid-specific (Mboat7-MSKO), deletion of Mboat7 exacerbates ethanol-induced liver injury. Lipidomic profiling reveals a reorganization of the hepatic lipidome in Mboat7-HSKO mice, characterized by increased endosomal/lysosomal lipids. Ethanol-exposed Mboat7-HSKO mice exhibit dysregulated autophagic flux and lysosomal biogenesis, associated with impaired transcription factor EB-mediated lysosomal biogenesis and autophagosome accumulation. This study provides mechanistic insights into how MBOAT7 influences ALD progression through dysregulation of lysosomal biogenesis and autophagic flux, highlighting hepatocyte-specific MBOAT7 loss as a key driver of ethanol-induced liver injury.
Keywords: MBOAT7; alcohol-associated liver disease; autophagy; medicine; mouse.
© 2023, Varadharajan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
VV, IR, WM, RJ, RB, AH, MM, EH, AB, SL, KG, RH, IJ, VP, JD, NW, SD, DS, OR, DA, JS, LN No competing interests declared, JS, JB Reviewing editor, eLife
Figures



Update of
-
Membrane Bound O-Acyltransferase 7 (MBOAT7) Shapes Lysosomal Lipid Homeostasis and Function to Control Alcohol-Associated Liver Injury.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 10:2023.09.26.559533. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.26.559533. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Apr 22;12:RP92243. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92243. PMID: 37808828 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Alharthi J, Bayoumi A, Thabet K, Pan Z, Gloss BS, Latchoumanin O, Lundberg M, Twine NA, McLeod D, Alenizi S, Adams LA, Weltman M, Berg T, Liddle C, George J, Eslam M. A metabolic associated fatty liver disease risk variant in MBOAT7 regulates toll like receptor induced outcomes. Nature Communications. 2022;13:7430. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35158-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK120679/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148158/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA026938/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL147823/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK133479/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK130227/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS133812/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK128022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA024333/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001998/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128268/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA026264/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

