Psychometric Properties of the Metacognitions About Online Gaming Scale in the Chinese Population and Its Relationship With Internet Gaming Disorder: Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 38648634
- PMCID: PMC11074897
- DOI: 10.2196/45985
Psychometric Properties of the Metacognitions About Online Gaming Scale in the Chinese Population and Its Relationship With Internet Gaming Disorder: Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Metacognitions about online gaming have been shown to be correlated with Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD). Knowledge of metacognitions about online gaming can help to understand IGD. The Metacognitions about Online Gaming Scale (MOGS) is a reliable and valid tool to measure specific metacognitions about online gaming in both adults and adolescents, which is lacking in China.
Objective: This study was conducted to assess the psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the MOGS (C-MOGS) and its relationship with IGD in the Chinese population.
Methods: A total of 772 Chinese individuals (age: mean 21.70, SD 8.81 years; age range: 13-57 years; 458/772, 59.3% male) completed a web-based questionnaire survey, including the C-MOGS and a battery of validated scales measuring IGD, gaming motives, depression, and anxiety.
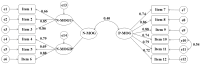
Results: Through exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses, the 3-factor structure was confirmed to have adequate model fit and internal consistency reliability (Cronbach α≥.799, Guttman split-half coefficients≥0.754). Concurrent validity of the C-MOGS was supported by its correlations with IGD (P<.001), gaming motives (P<.001), depression (P<.001), and anxiety (P<.001). Furthermore, the incremental validity analysis showed that the C-MOGS predicted 13% of the variance in IGD while controlling for gender, age, weekly gaming hours, gaming motives, depression, and anxiety.
Conclusions: This study provides evidence that the psychometric properties of the C-MOGS are appropriate and emphasizes its positive association with IGD. The C-MOGS is a reliable and valid instrument for mental health workers to assess metacognitions about online gaming in the Chinese population.
Keywords: Chinese; Internet Gaming Disorder; metacognition; metacognitions about online gaming; psychometric properties.
©Shuhong Lin, Xinxin Chen, Linxiang Tan, Zhenjiang Liao, Yifan Li, Ying Tang, Qiuping Huang, Hongxian Shen. Originally published in JMIR Serious Games (https://games.jmir.org), 22.04.2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of the metacognitions about online gaming scale (MOGS) among Chinese gamers.Addict Behav. 2022 Jun;129:107255. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2022.107255. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Addict Behav. 2022. PMID: 35091197
-
Metacognitions as a predictor of online gaming in adolescents: Psychometric properties of the metacognitions about online gaming scale among Iranian adolescents.Addict Behav. 2021 Jul;118:106904. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.106904. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Addict Behav. 2021. PMID: 33743493
-
The relationships between positive/negative metacognitions and Internet gaming disorder among Chinese adult gamers: Cross-sectional and longitudinal evidence.Addict Behav. 2025 Apr;163:108245. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2024.108245. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Addict Behav. 2025. PMID: 39756127
-
"I have no control over how much time I play" the metacognitions about online gaming scale: Evidence from a cross-cultural validation among Israeli adolescents.Addict Behav. 2023 Jun;141:107638. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2023.107638. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Addict Behav. 2023. PMID: 36746106
-
A systematic review of metacognitions in Internet Gaming Disorder and problematic Internet, smartphone and social networking sites use.Clin Psychol Psychother. 2021 Nov;28(6):1494-1508. doi: 10.1002/cpp.2588. Epub 2021 May 4. Clin Psychol Psychother. 2021. PMID: 33783920 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Interaction Effects Between Low Self-Control and Meaning in Life on Internet Gaming Disorder Symptoms and Functioning in Chinese Adolescents: Cross-Sectional Latent Moderated Structural Equation Modeling Study.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Nov 4;26:e59490. doi: 10.2196/59490. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39496163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flavell JH. Metacognition and cognitive monitoring: A new area of cognitive-developmental inquiry. American Psychologist. 1979;34(10):906–911. doi: 10.1037//0003-066x.34.10.906. - DOI
-
- Metcalfe J. Metacognitive judgments and control of study. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2009 Jun 01;18(3):159–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8721.2009.01628.x. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/19750138 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heyes C, Bang D, Shea N, Frith CD, Fleming SM. Knowing ourselves together: the cultural origins of metacognition. Trends Cogn Sci. 2020 May;24(5):349–362. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2020.02.007. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1364-6613(20)30059-0 S1364-6613(20)30059-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schraw G, Moshman D. Metacognitive theories. Educ Psychol Rev. 1995 Dec;7(4):351–371. doi: 10.1007/bf02212307. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

