Mrj is a chaperone of the Hsp40 family that regulates Orb2 oligomerization and long-term memory in Drosophila
- PMID: 38648719
- PMCID: PMC11034981
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002585
Mrj is a chaperone of the Hsp40 family that regulates Orb2 oligomerization and long-term memory in Drosophila
Abstract
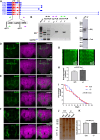
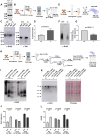
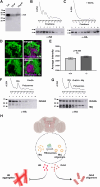
Orb2 the Drosophila homolog of cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding (CPEB) protein forms prion-like oligomers. These oligomers consist of Orb2A and Orb2B isoforms and their formation is dependent on the oligomerization of the Orb2A isoform. Drosophila with a mutation diminishing Orb2A's prion-like oligomerization forms long-term memory but fails to maintain it over time. Since this prion-like oligomerization of Orb2A plays a crucial role in the maintenance of memory, here, we aim to find what regulates this oligomerization. In an immunoprecipitation-based screen, we identify interactors of Orb2A in the Hsp40 and Hsp70 families of proteins. Among these, we find an Hsp40 family protein Mrj as a regulator of the conversion of Orb2A to its prion-like form. Mrj interacts with Hsp70 proteins and acts as a chaperone by interfering with the aggregation of pathogenic Huntingtin. Unlike its mammalian homolog, we find Drosophila Mrj is neither an essential gene nor causes any gross neurodevelopmental defect. We observe a loss of Mrj results in a reduction in Orb2 oligomers. Further, Mrj knockout exhibits a deficit in long-term memory and our observations suggest Mrj is needed in mushroom body neurons for the regulation of long-term memory. Our work implicates a chaperone Mrj in mechanisms of memory regulation through controlling the oligomerization of Orb2A and its association with the translating ribosomes.
Copyright: © 2024 Desai et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Contribution of Orb2A stability in regulated amyloid-like oligomerization of Drosophila Orb2.PLoS Biol. 2014 Feb 11;12(2):e1001786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001786. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Biol. 2014. PMID: 24523662 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila CPEB Orb2A mediates memory independent of Its RNA-binding domain.Neuron. 2012 Oct 18;76(2):383-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.08.028. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 23083740 Free PMC article.
-
Micro-electron diffraction structure of the aggregation-driving N terminus of Drosophila neuronal protein Orb2A reveals amyloid-like β-sheets.J Biol Chem. 2022 Oct;298(10):102396. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102396. Epub 2022 Aug 18. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35988647 Free PMC article.
-
Chaperone networks in protein disaggregation and prion propagation.J Struct Biol. 2012 Aug;179(2):152-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.05.002. Epub 2012 May 10. J Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22580344 Review.
-
Implications of the Orb2 Amyloid Structure in Huntington's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 21;21(18):6910. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186910. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32967102 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Two novel DnaJ chaperone proteins CG5001 and P58IPK regulate the pathogenicity of Huntington's disease related aggregates.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 6;14(1):20867. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71065-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39242711 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic Huntingtin aggregates alter actin organization and cellular stiffness resulting in stalled clathrin-mediated endocytosis.Elife. 2024 Oct 9;13:e98363. doi: 10.7554/eLife.98363. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39382268 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

