The IRE1α-XBP1 arm of the unfolded protein response is a host factor activated in SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 38648902
- PMCID: PMC12191402
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167193
The IRE1α-XBP1 arm of the unfolded protein response is a host factor activated in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
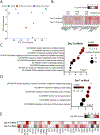
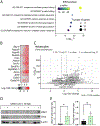
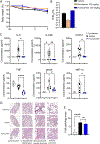
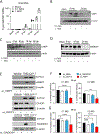
SARS-CoV-2 infection can cause severe pneumonia, wherein exacerbated inflammation plays a major role. This is reminiscent of the process commonly termed cytokine storm, a condition dependent on a disproportionated production of cytokines. This state involves the activation of the innate immune response by viral patterns and coincides with the biosynthesis of the biomass required for viral replication, which may overwhelm the capacity of the endoplasmic reticulum and drive the unfolded protein response (UPR). The UPR is a signal transduction pathway composed of three branches that is initiated by a set of sensors: inositol-requiring protein 1 (IRE1), protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase (PERK), and activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6). These sensors control adaptive processes, including the transcriptional regulation of proinflammatory cytokines. Based on this background, the role of the UPR in SARS-CoV-2 replication and the ensuing inflammatory response was investigated using in vivo and in vitro models of infection. Mice and Syrian hamsters infected with SARS-CoV-2 showed a sole activation of the Ire1α-Xbp1 arm of the UPR associated with a robust production of proinflammatory cytokines. Human lung epithelial cells showed the dependence of viral replication on the expression of UPR-target proteins branching on the IRE1α-XBP1 arm and to a lower extent on the PERK route. Likewise, activation of the IRE1α-XBP1 branch by Spike (S) proteins from different variants of concern was a uniform finding. These results show that the IRE1α-XBP1 system enhances viral replication and cytokine expression and may represent a potential therapeutic target in SARS-CoV-2 severe pneumonia.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cytokines; Fluvoxamine; Pneumonia; TLR; Transcription factors; Unfolded protein response; Variants of concern; Viral sepsis.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The A.G.S. laboratory has received research support from GSK, Pfizer, Senhwa Biosciences, Kenall Manufacturing, Blade Therapeutics, Avimex, Johnson & Johnson, Dynavax, 7Hills Pharma, Pharmamar, ImmunityBio, Accurius, Nanocomposix, Hexamer, N-fold LLC, Model Medicines, Atea Pharma, Applied Biological Laboratories and Merck, outside of the reported work. A.G.S. has consulting agreements for the following companies involving cash and/or stock: Castlevax, Amovir, Vivaldi Biosciences, Contrafect, 7Hills Pharma, Avimex, Pagoda, Accurius, Esperovax, Farmak, Applied Biological Laboratories, Pharmamar, CureLab Oncology, CureLab Veterinary, Synairgen, Paratus and Pfizer, outside of the reported work. A.G.S. has been an invited speaker in meeting events organized by Seqirus, Janssen, Abbott and Astrazeneca. A.G.S is inventor on patents and patent applications on the use of antivirals and vaccines for the treatment and prevention of virus infections and cancer, owned by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, outside of the reported work. A.M. is the creator of Omics Bioinformatics S.L. and owns all the stocks of this company. The M.S. laboratory has received unrelated research funding in sponsored research agreements from 7Hills Pharma, ArgenX N.V., Moderna and Phio Pharmaceuticals, which has no competing interest with this work. The article reflects the views of the authors and does not represent the views or policies of the FDA. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

