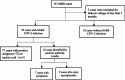
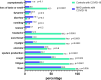
Clinical characteristics and outcomes of maintenance hemodialysis patients with COVID-19 during the Omicron wave of the pandemic in Beijing: a single center retrospective study
- PMID: 38649863
- PMCID: PMC11036696
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-024-03575-1
Clinical characteristics and outcomes of maintenance hemodialysis patients with COVID-19 during the Omicron wave of the pandemic in Beijing: a single center retrospective study
Abstract
Background: The clinical manifestations and prognosis of hemodialysis patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) during the Omicron wave of the pandemic infection were still unclear. This study investigated the clinical characteristics of patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) infected with it.
Methods: This retrospective single-center study included 151 patients undergoing MHD. Healthcare workers were selected as control group were assessed from December 1, 2022 to March 31, 2023. Clinical data, laboratory test results, treatment protocols, and prognoses were collected and analyzed.
Results: The study population included 146 patients with MHD, 93 (63.7%) of whom were infected with SARS-CoV-2. The number of non-severe, severe, and critical cases was 84 (90.3%), 4 (4.3%), and 5 (5.3%), respectively. Six patients (6.5%) died during the study period. The main symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection, including fever, cough, and fatigue, were less common in patients with MHD than the controls. During SARS-CoV-2 infection, the C-reactive protein (2.9 vs. 11.8 mg/dl, p < 0.0001) and ferritin levels(257.7 vs. 537 ng/l, p < 0.0001) were elevated. The hemoglobin(113vs 111 g/L, p = 0.0001) and albumin levels(39.4 vs. 36.1 g/L, p < 0.0001) decreased. Generally, it took two months for the hemoglobin levels to recover. Positivity rate for SARS-COV-2 serum immunoglobin G (IgG) antibodies and IgG titers were lower in dialysis patients than the controls. Age was positively associated with disease severity, while age and hyponatremia were associated with death.
Conclusions: Patients with MHD and COVID-19 were primarily classified as non-severe. SARS-CoV-2 infection would soon lead to the increase of inflammation related acute response protein in dialysis patients, and then lead to the decrease of hemoglobin and albumin. About 9.6% in HD patients were severe cases and had poor prognosis. Advanced age and hyponatremia were associated with disease severity and prognosis.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); Maintenance hemodialysis (MHD); Omicron variant; Prognosis; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-cov-2).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Infection status and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in maintenance hemodialysis patients in Wuhan during the omicron pandemic.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Sep 8;102(36):e35063. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035063. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37682194 Free PMC article.
-
Serologic Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Hemodialysis Centers: A Multicenter Retrospective Study in Wuhan, China.Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Oct;76(4):490-499.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.06.008. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020. PMID: 32628990 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Infections among Vaccinated Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients: Outcomes and Comparison to Delta Variant.Nephron. 2024;148(9):601-608. doi: 10.1159/000536521. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Nephron. 2024. PMID: 38484724 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality and risk factors for COVID-19 in hemodialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Prog. 2022 Jul-Sep;105(3):368504221110858. doi: 10.1177/00368504221110858. Sci Prog. 2022. PMID: 35775141 Free PMC article.
-
The laboratory parameters in predicting the severity and death of COVID-19 patients: Future pandemic readiness strategies.Biomol Biomed. 2024 Mar 11;24(2):238-255. doi: 10.17305/bb.2023.9540. Biomol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 37712883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hsu CM, Weiner DE, Aweh G, Miskulin DC, Manley HJ, Stewart C, Ladik V, Hosford J, Lacson EC, Johnson DS, et al. COVID-19 among US Dialysis patients: risk factors and outcomes from a National Dialysis Provider. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021;77(5):748–e756741. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.01.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous