Itaconate alleviates anesthesia/surgery-induced cognitive impairment by activating a Nrf2-dependent anti-neuroinflammation and neurogenesis via gut-brain axis
- PMID: 38649932
- PMCID: PMC11034021
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-024-03103-w
Itaconate alleviates anesthesia/surgery-induced cognitive impairment by activating a Nrf2-dependent anti-neuroinflammation and neurogenesis via gut-brain axis
Abstract
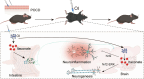
Background: Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) is a common neurological complication of anesthesia and surgery in aging individuals. Neuroinflammation has been identified as a hallmark of POCD. However, safe and effective treatments of POCD are still lacking. Itaconate is an immunoregulatory metabolite derived from the tricarboxylic acid cycle that exerts anti-inflammatory effects by activating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway. In this study, we investigated the effects and underlying mechanism of 4-octyl itaconate (OI), a cell-permeable itaconate derivative, on POCD in aged mice.
Methods: A POCD animal model was established by performing aseptic laparotomy in 18-month-old male C57BL/6 mice under isoflurane anesthesia while maintaining spontaneous ventilation. OI was intraperitoneally injected into the mice after surgery. Primary microglia and neurons were isolated and treated to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), isoflurane, and OI. Cognitive function, neuroinflammatory responses, as well as levels of gut microbiota and their metabolites were evaluated. To determine the mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of OI in POCD, ML385, an antagonist of Nrf2, was administered intraperitoneally. Cognitive function, neuroinflammatory responses, endogenous neurogenesis, neuronal apoptosis, and Nrf2/extracellular signal-related kinases (ERK) signaling pathway were evaluated.
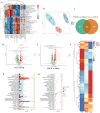
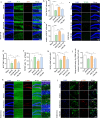
Results: Our findings revealed that OI treatment significantly alleviated anesthesia/surgery-induced cognitive impairment, concomitant with reduced levels of the neuroinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-6, as well as suppressed activation of microglia and astrocytes in the hippocampus. Similarly, OI treatment inhibited the expression of IL-1β and IL-6 in LPS and isoflurane-induced primary microglia in vitro. Intraperitoneal administration of OI led to alterations in the gut microbiota and promoted the production of microbiota-derived metabolites associated with neurogenesis. We further confirmed that OI promoted endogenous neurogenesis and inhibited neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of aged mice. Mechanistically, we observed a decrease in Nrf2 expression in hippocampal neurons both in vitro and in vivo, which was reversed by OI treatment. We found that Nrf2 was required for OI treatment to inhibit neuroinflammation in POCD. The enhanced POCD recovery and promotion of neurogenesis triggered by OI exposure were, at least partially, mediated by the activation of the Nrf2/ERK signaling pathway.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that OI can attenuate anesthesia/surgery-induced cognitive impairment by stabilizing the gut microbiota and activating Nrf2 signaling to restrict neuroinflammation and promote neurogenesis. Boosting endogenous itaconate or supplementation with exogenous itaconate derivatives may represent novel strategies for the treatment of POCD.
Keywords: 4-octyl itaconate; Gut microbiota; Itaconate; Neurogenesis; Neuroinflammation; Nrf2; Postoperative cognitive dysfunction.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Wei P, Zheng Q, Liu H, et al. Nicotine-induced neuroprotection against cognitive dysfunction after partial hepatectomy involves activation of BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway and inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling pathway in aged rats. Nicotine Tob Res. 2018;20(4):515–522. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntx157. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

