Targeted delivery of HSP90 inhibitors for efficient therapy of CD44-positive acute myeloid leukemia and solid tumor-colon cancer
- PMID: 38649957
- PMCID: PMC11036589
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02460-1
Targeted delivery of HSP90 inhibitors for efficient therapy of CD44-positive acute myeloid leukemia and solid tumor-colon cancer
Abstract
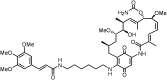
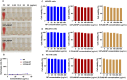
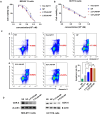
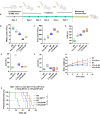
Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) is overexpressed in numerous cancers, promotes the maturation of numerous oncoproteins and facilitates cancer cell growth. Certain HSP90 inhibitors have entered clinical trials. Although less than satisfactory clinical effects or insurmountable toxicity have compelled these trials to be terminated or postponed, these results of preclinical and clinical studies demonstrated that the prospects of targeting therapeutic strategies involving HSP90 inhibitors deserve enough attention. Nanoparticulate-based drug delivery systems have been generally supposed as one of the most promising formulations especially for targeting strategies. However, so far, no active targeting nano-formulations have succeeded in clinical translation, mainly due to complicated preparation, complex formulations leading to difficult industrialization, incomplete biocompatibility or nontoxicity. In this study, HSP90 and CD44-targeted A6 peptide functionalized biomimetic nanoparticles (A6-NP) was designed and various degrees of A6-modification on nanoparticles were fabricated to evaluate targeting ability and anticancer efficiency. With no excipients, the hydrophobic HSP90 inhibitor G2111 and A6-conjugated human serum albumin could self-assemble into nanoparticles with a uniform particle size of approximately 200 nm, easy fabrication, well biocompatibility and avoidance of hepatotoxicity. Besides, G2111 encapsulated in A6-NP was only released less than 5% in 12 h, which may avoid off-target cell toxicity before entering into cancer cells. A6 peptide modification could significantly enhance uptake within a short time. Moreover, A6-NP continues to exert the broad anticancer spectrum of Hsp90 inhibitors and displays remarkable targeting ability and anticancer efficacy both in hematological malignancies and solid tumors (with colon tumors as the model cancer) both in vitro and in vivo. Overall, A6-NP, as a simple, biomimetic and active dual-targeting (CD44 and HSP90) nanomedicine, displays high potential for clinical translation.
Keywords: Active targeting nanoparticles; Acute myeloid leukemia; CD44; Heat shock protein 90; Solid tumor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Hybrid Nanoparticles Modified by Hyaluronic Acid Loading an HSP90 Inhibitor as a Novel Delivery System for Subcutaneous and Orthotopic Colon Cancer Therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Mar 2;16:1743-1755. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S275805. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33688189 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced in vivo antitumor efficacy of dual-functional peptide-modified docetaxel nanoparticles through tumor targeting and Hsp90 inhibition.J Control Release. 2016 Jan 10;221:26-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.11.029. Epub 2015 Nov 28. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 26643616
-
CD44-Specific A6 Short Peptide Boosts Targetability and Anticancer Efficacy of Polymersomal Epirubicin to Orthotopic Human Multiple Myeloma.Adv Mater. 2019 Nov;31(46):e1904742. doi: 10.1002/adma.201904742. Epub 2019 Sep 27. Adv Mater. 2019. PMID: 31560141
-
Heat shock protein 90 - a potential target in the treatment of human acute myelogenous leukemia.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009 Sep;9(6):761-76. doi: 10.2174/156800909789271486. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19754360 Review.
-
Heat shock proteins and cancer: How can nanomedicine be harnessed?J Control Release. 2017 Feb 28;248:133-143. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.01.013. Epub 2017 Jan 11. J Control Release. 2017. PMID: 28088573 Review.
Cited by
-
Heat shock proteins as hallmarks of cancer: insights from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies.J Hematol Oncol. 2024 Sep 4;17(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01601-1. J Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39232809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano-formulations in disease therapy: designs, advances, challenges, and future directions.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 30;23(1):396. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03442-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40448105 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu L, Deng Y, Zheng Z, Deng Z, Zhang J, Li J, Liang M, Zhou X, Tan W, Yang H, Neckers LM, Zou F, Chen X. Hsp90 inhibitor STA9090 sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Hyperthermia-Induced DNA damage by suppressing DNA-PKcs protein Stability and mRNA transcription, Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021;20:1880–92. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-21-0215. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xu Q, Tu J, Dou C, Zhang J, Yang L, Liu X, Lei K, Liu Z, Wang Y, Li L, Bao H, Wang J, Tu K. HSP90 promotes cell glycolysis, proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by regulating PKM2 abundance via Thr-328 phosphorylation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:178. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0748-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

