Ki-67 is necessary during DNA replication for fork protection and genome stability
- PMID: 38649976
- PMCID: PMC11034166
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-024-03243-5
Ki-67 is necessary during DNA replication for fork protection and genome stability
Abstract
Background: The proliferation antigen Ki-67 has been widely used in clinical settings for cancer staging for many years, but investigations on its biological functions have lagged. Recently, Ki-67 has been shown to regulate both the composition of the chromosome periphery and chromosome behaviour in mitosis as well as to play a role in heterochromatin organisation and gene transcription. However, how the different roles for Ki-67 across the cell cycle are regulated and coordinated remain poorly understood. The progress towards understanding Ki-67 function have been limited by the tools available to deplete the protein, coupled to its abundance and fluctuation during the cell cycle.
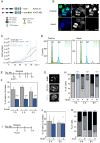
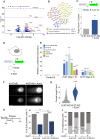
Results: Here, we use a doxycycline-inducible E3 ligase together with an auxin-inducible degron tag to achieve a rapid, acute and homogeneous degradation of Ki-67 in HCT116 cells. This system, coupled with APEX2 proteomics and phospho-proteomics approaches, allows us to show that Ki-67 plays a role during DNA replication. In its absence, DNA replication is severely delayed, the replication machinery is unloaded, causing DNA damage that is not sensed by the canonical pathways and dependent on HUWE1 ligase. This leads to defects in replication and sister chromatids cohesion, but it also triggers an interferon response mediated by the cGAS/STING pathway in all the cell lines tested.
Conclusions: We unveil a new function of Ki-67 in DNA replication and genome maintenance that is independent of its previously known role in mitosis and gene regulation.
Keywords: AID tag; APEX2; DNA damage; DNA replication; HUWE1; Interferon response; Ki-67; Sister chromatid cohesion.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Dowsett M, Nielsen TO, A'Hern R, Bartlett J, Coombes RC, Cuzick J, Ellis M, Henry NL, Hugh JC, Lively T, et al. Assessment of Ki67 in breast cancer: recommendations from the International Ki67 in Breast Cancer working group. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103:1656–1664. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr393. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duregon E, Bertero L, Pittaro A, Soffietti R, Ruda R, Trevisan M, Papotti M, Ventura L, Senetta R, Cassoni P. Ki-67 proliferation index but not mitotic thresholds integrates the molecular prognostic stratification of lower grade gliomas. Oncotarget. 2016;7:21190–21198. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8498. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

