Efficacy and Safety of Alogliptin-Pioglitazone Combination for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Poorly Controlled with Metformin: A Multicenter, Double-Blind Randomized Trial
- PMID: 38650099
- PMCID: PMC11449827
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0259
Efficacy and Safety of Alogliptin-Pioglitazone Combination for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Poorly Controlled with Metformin: A Multicenter, Double-Blind Randomized Trial
Abstract
Backgruound: Guidelines for switching to triple combination therapy directly after monotherapy failure are limited. This study investigated the efficacy, long-term sustainability, and safety of either mono or dual add-on therapy using alogliptin and pioglitazone for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who did not achieve their target glycemic range with metformin monotherapy.
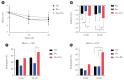
Methods: The Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Combination Therapy in Korea (PEAK) was a multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized trial. A total of 214 participants were randomized to receive alogliptin+pioglitazone (Alo+Pio group, n=70), alogliptin (Alo group, n=75), or pioglitazone (Pio group, n=69). The primary outcome was the difference in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels between the three groups at baseline to 24 weeks. For durability, the achievement of HbA1c levels <7% and <6.5% was compared in each group. The number of adverse events was investigated for safety.
Results: After 24 weeks of treatment, the change of HbA1c in the Alo+Pio, Alo, and Pio groups were -1.38%±0.08%, -1.03%±0.08%, and -0.84%±0.08%, respectively. The Alo+Pio group had significantly lower HbA1c levels than the other groups (P=0.0063, P<0.0001) and had a higher proportion of patients with target HbA1c achievement. In addition, insulin sensitivity and β-cell function, lipid profiles, and other metabolic indicators were also improved. There were no significant safety issues in patients treated with triple combination therapy.
Conclusion: Early combination triple therapy showed better efficacy and durability than the single add-on (dual) therapy. Therefore, combination therapy with metformin, alogliptin, and pioglitazone is a valuable early treatment option for T2DM poorly controlled with metformin monotherapy.
Keywords: Alogliptin; Diabetes mellitus, type 2; Glycated hemoglobin; Hypoglycemic agents; Metformin; Pioglitazone.
Conflict of interest statement
The study received financial support from Takeda Pharmaceuticals Korea Co., Ltd. in the form of an investigator-initiated study grant. The funder had no involvement in the study’s design, data collection, statistical analysis, data interpretation, decision to publish, or the preparation of the manuscript. It should be noted that one of the co-authors, Yoon-Hee Choi, holds the position of CEO at Medical Excellence, a CRO (Contract Research Organization) company that received funding from Takeda Pharmaceuticals Korea. Yoon-Hee Choi participated in statistical analysis of the data produced by this study.
Kyung Mook Choi has been editor-in-chief of the
Figures
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. - PubMed
-
- Matthews DR, Paldanius PM, Proot P, Chiang Y, Stumvoll M, Del Prato S, et al. Glycaemic durability of an early combination therapy with vildagliptin and metformin versus sequential metformin monotherapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (VERIFY): a 5-year, multicentre, randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet. 2019;394:1519–29. - PubMed
-
- Abdul-Ghani MA, Puckett C, Triplitt C, Maggs D, Adams J, Cersosimo E, et al. Initial combination therapy with metformin, pioglitazone and exenatide is more effective than sequential add-on therapy in subjects with new-onset diabetes: results from the Efficacy and Durability of Initial Combination Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes (EDICT): a randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17:268–75. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

