Computational design of highly stable and soluble alcohol dehydrogenase for NADPH regeneration
- PMID: 38650213
- PMCID: PMC10992930
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-021-00362-w
Computational design of highly stable and soluble alcohol dehydrogenase for NADPH regeneration
Abstract
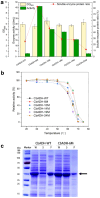
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), as a well-known cofactor, is widely used in the most of enzymatic redox reactions, playing an important role in industrial catalysis. However, the absence of a comparable method for efficient NADP+ to NADPH cofactor regeneration radically impairs efficient green chemical synthesis. Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) enzymes, allowing the in situ regeneration of the redox cofactor NADPH with high specific activity and easy by-product separation process, are provided with great industrial application potential and research attention. Accordingly, herein a NADP+-specific ADH from Clostridium beijerinckii was selected to be engineered for cofactor recycle, using an automated algorithm named Protein Repair One-stop Shop (PROSS). The mutant CbADH-6M (S24P/G182A/G196A/H222D/S250E/S254R) exhibited a favorable soluble and highly active expression with an activity of 46.3 U/mL, which was 16 times higher than the wild type (2.9 U/mL), and a more stable protein conformation with an enhanced thermal stability: Δ = + 3.6 °C (temperature of 50% inactivation after incubation for 60 min). Furthermore, the activity of CbADH-6M was up-graded to 2401.8 U/mL by high cell density fermentation strategy using recombinant Escherichia coli, demonstrating its industrial potential. Finally, the superb efficiency for NADPH regeneration of the mutant enzyme was testified in the synthesis of some fine chiral aromatic alcohols coupling with another ADH from Lactobacillus kefir (LkADH).
Keywords: Alcohol dehydrogenase; Chiral alcohols; Computational design; NADPH regeneration; Soluble expression.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Bastos FDM, dos Santos AG, Jones J, Oestreicher EG, Pinto GF, Paiva LMC. Three different coupled enzymatic systems for in situ regeneration of NADPH. Biotechnol Techniques. 1999;13(10):661–664. doi: 10.1023/A:1008957711413. - DOI
-
- Benítez-Mateos AI, San Sebastian E, Ríos-Lombardía N, Morís F, González-Sabín J, López-Gallego F. Asymmetric reduction of prochiral ketones by using self-sufficient heterogeneous biocatalysts based on NADPH-Dependent Ketoreductases. Chem Eur J. 2017;23(66):16843–16852. doi: 10.1002/chem.201703475. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bogin O, Levin I, Hacham Y, Tel-Or S, Peretz M, Frolow F, Burstein Y. Structural basis for the enhanced thermal stability of alcohol dehydrogenase mutants from the mesophilic bacterium Clostridium beijerinckii: contribution of salt bridging. Protein Sci. 2002;11(11):2561–2574. doi: 10.1110/ps.0222102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown KA, Wilker MB, Boehm M, Hamby H, Dukovic G, King PW. Photocatalytic regeneration of nicotinamide cofactors by quantum dot-enzyme biohybrid complexes. ACS Catalysis. 2016;6(4):2201–2204. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b02850. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

