Pulp and paper mill wastes: utilizations and prospects for high value-added biomaterials
- PMID: 38650230
- PMCID: PMC10991416
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-021-00385-3
Pulp and paper mill wastes: utilizations and prospects for high value-added biomaterials
Abstract
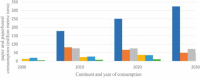
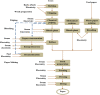
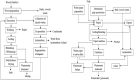
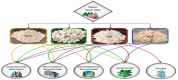
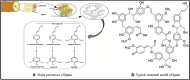
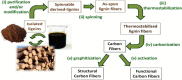
A wide variety of biomass is available all around the world. Most of the biomass exists as a by-product from manufacturing industries. Pulp and paper mills contribute to a higher amount of these biomasses mostly discarded in the landfills creating an environmental burden. Biomasses from other sources have been used to produce different kinds and grades of biomaterials such as those used in industrial and medical applications. The present review aims to investigate the availability of biomass from pulp and paper mills and show sustainable routes for the production of high value-added biomaterials. The study reveals that using conventional and integrated biorefinery technology the ample variety and quantity of waste generated from pulp and paper mills can be converted into wealth. As per the findings of the current review, it is shown that high-performance carbon fiber and bioplastic can be manufactured from black liquor of pulping waste; the cellulosic waste from sawdust and sludge can be utilized for the synthesis of CNC and regenerated fibers such as viscose rayon and acetate; the mineral-based pulping wastes and fly ash can be used for manufacturing of different kinds of biocomposites. The different biomaterials obtained from the pulp and paper mill biomass can be used for versatile applications including conventional, high performance, and smart materials. Through customization and optimization of the conversion techniques and product manufacturing schemes, a variety of engineering materials can be obtained from pulp and paper mill wastes realizing the current global waste to wealth developmental approach.
Keywords: Biomass; Biomaterials; Biorefinery; High value-added; Paper mill; Pulping waste.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Ai T, Dong X, Ai D. Process for causticizing green liquor in chemical recovery from black liquor in alkaline pulping. London: Google Patents; 2007.
-
- Akampumuza O, Wambua PM, Ahmed A, Li W, Qin XH. Review of the applications of biocomposites in the automotive industry. Polym Compos. 2017;38:2553–2569. doi: 10.1002/pc.23847. - DOI
-
- Akbari M, Oyedum AO, Jain S, Kumar A. Options for the conversion of pulp and paper mill by-products in Western Canada. Sustainable Energy Technol Assess. 2018;26:83–92. doi: 10.1016/j.seta.2017.10.003. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

