Development of aqueous two-phase systems-based approaches for the selective recovery of metalloproteases and phospholipases A2 toxins from Crotalus molossus nigrescens venom
- PMID: 38650265
- PMCID: PMC10992436
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-021-00487-y
Development of aqueous two-phase systems-based approaches for the selective recovery of metalloproteases and phospholipases A2 toxins from Crotalus molossus nigrescens venom
Abstract
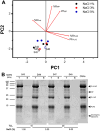
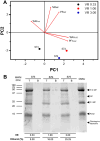
Snake venoms are rich sources of proteins with potential biotechnological and pharmaceutical applications. Among them, metalloproteases (MPs) and phospholipases A2 (PLA2) are the most abundant. Their isolation involves a multistep chromatographic approach, which has proven to be effective, however implies high operating costs and long processing times. In this study, a cost-effective and simple method based on aqueous two-phase systems (ATPS) was developed to recover MPs and PLA2 from Crotalus molossus nigrescens venom. A system with PEG 400 g mol-1, volume ratio (VR) 1, tie line length (TLL) 25% w/w and pH 7 showed the best performance for PLA2 recovery. In systems with PEG 400 g mol-1, VR 1, TLL 15% w/w, pH 7 and 1 and 3% w/w of NaCl, selective recovery of MP subtype P-III was achieved; whereas, in a system with PEG 400 g mol-1, VR 1, TLL 25% w/w and pH 8.5, MP subtypes P-I and P-III were recovered. Due to their low costs, ethanol-salt systems were also evaluated, however, failed to differentially partition PLA2 and MPs. The use of ATPS could contribute to the simplification and cost reduction of protein isolation processes from snake venoms and other toxin fluids, as well as potentially aid their biochemical, proteomic and biological analyses.
Keywords: Crotalus molossus nigrescens; Aqueous two-phase systems; Metalloproteases; Phospholipases A2; Recovery; Venom.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There authors declare that they have no competing of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aguilar O, Albiter V, Serrano-Carreón L, Rito-Palomares M. Direct comparison between ion-exchange chromatography and aqueous two-phase processes for the partial purification of penicillin acylase produced by E. coli. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2006;835:77–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.03.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Babu BR, Rastogi NK, Raghavarao KSMS. Liquid-liquid extraction of bromelain and polyphenol oxidase using aqueous two-phase system. Chem Eng Process. 2008;47:83–89. doi: 10.1016/j.cep.2007.08.006. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

