Vinasse: from a residue to a high added value biopolymer
- PMID: 38650284
- PMCID: PMC10992345
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-021-00476-1
Vinasse: from a residue to a high added value biopolymer
Abstract
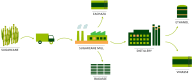
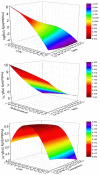
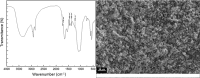
This work aimed to study the feasibility of using vinasse for polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) production by Bacillus megaterium. To optimize the culture medium, a Box-Behnken design was employed considering carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (Ph) concentrations as independent variables and PHB productivity as the response variable. The productivity decreased when C or N were increased, probably due to the presence of phenolic compounds and the limitation of N for the production of PHB by Bacillus sp. bacteria. An additional experimental design to optimize the C/N ratio and growing conditions (fermentation time and temperature) was carried out. Fermentation time had a statistically significant effect on PHB productivity reaching 10.6 mg/L h. On the other hand, the variability in physicochemical properties of vinasse samples led to significant differences in PHB productivity. Lower productivity values were obtained when vinasse had higher values of DBO. Therefore, biopolymers production from vinasse is a feasible alternative to valorize this bioethanol by-product.
Keywords: Bacillus megaterium; Culture medium optimization; Microbial fermentation; Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB); Vinasse.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Acosta-Cárdenas A, Alcaraz-zapata W, Cardona-Betancur M. Sugarcane molasses and vinasse as a substrate for polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) production. Melazas y vinaza de la caña de azúcar como sustrato para la producción de polihidroxialcanoatos (PHA) RevistasUnalEduCo. 2018;85:220–225.
-
- Amini M, Yousefi-massumabad H, Younesi H, Abyar H. Production of the polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolymer by Cupriavidus necator using beer brewery wastewater containing maltose as a primary carbon source. J Environ Chem Eng. 2020;8:103588. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.103588. - DOI
-
- Andrady AL. Persistence of plastic litter in the oceans. In: Bergmann M, Gutow L, Klages M, editors. Marine anthropogenic litter. Cham: Springer; 2015. pp. 57–72.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

