Effects of resistance training on sleep quality and disorders among individuals diagnosed with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 38650577
- PMCID: PMC11036080
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.7179
Effects of resistance training on sleep quality and disorders among individuals diagnosed with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Sleep disorders are often complained by cancer patients and can last years after the end of therapies, leading to different negative consequences. Non-pharmacological strategies such as exercise interventions may be considered to counteract this phenomenon. The literature supports the beneficial effects of aerobic training (AT), while evidence on resistance training (RT) is scarce. Accordingly, our systematic review aims to investigate the potential novel effect of RT on sleep outcomes in cancer survivors.
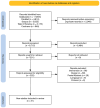
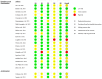
Methods: The literature search was conducted on MEDLINE (Pubmed), Web of Science, Scopus, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials databases, including only randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The screening procedure was conducted using the web-based software COVIDENCE. Sleep outcomes assessed through self-reported questionnaires or objective sleep measurements were extracted from RCTs recruiting cancer survivors of any age and gender, on or off treatment. The risk of bias (RoB) for each study was assessed using the Cochrane RoB 2 tool for RCTs. Meta-analytic syntheses were performed on sleep quality and insomnia.
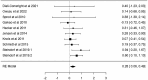
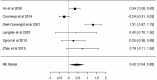
Results: A total of 21 studies were included in the review. Considering the mean percentage differences of all studies combined, promising positive results were found after combined aerobic and resistance exercise program (COMB) for sleep quality (-19%) and sleep disturbance (-17.3%). The meta-analysis results showed significant improvement for both sleep quality and insomnia (d = 0.28, SE: 0.11, Z = 2.51, p < 0.01, 95% CI: 0.07-0.49 and d = 0.43, SE: 0.20, Z = 2.18, p = 0.029, 95% CI: 0.07-0.49, respectively).
Conclusion: RT interventions of 60 minutes per session, performed 2-3 times a week for 12 weeks, with exercise intensity ranging from 60% to 80% of one-repetition maximum can be administered to cancer survivors, aiming to improve sleep outcomes.
Keywords: exercise oncology; insomnia; physical activity; quality of life; tumor.
© 2024 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society . The Global Cancer Burden; 2022. https://www.cancer.org/about‐us/our‐global‐health‐work/global‐cancer‐bur...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

