The Influence of Lifestyle on Academic Performance Among Health Profession Students at Umm Al-Qura University
- PMID: 38650788
- PMCID: PMC11033961
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.56759
The Influence of Lifestyle on Academic Performance Among Health Profession Students at Umm Al-Qura University
Abstract
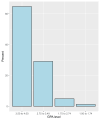
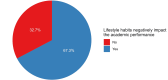
Background and aim A healthy lifestyle is defined as a way of living that reduces the likelihood of severe illness or early death. Factors required for a healthy lifestyle, such as regular physical activity, better sleep patterns, improved dietary habits, probable caffeine consumption, and decreased feelings of anxiety, are generally assumed to be important for high academic performance. This study aims to investigate the correlation between a healthy lifestyle and academic success among health profession students at Umm Al-Qura University, Saudi Arabia. By doing so, we could potentially lead to the implementation of targeted interventions to support students in achieving their best academic potential. Methods This is an observational cross-sectional study conducted among health profession students at Umm Al-Qura University. An online questionnaire was used to collect data on demographic information and the impact of lifestyle characteristics on academic performance from October to November 2023. Data were analyzed using RStudio (R version 4.3.1). Results A total of 652 students participated in the study. The majority were between the ages of 18 and 25 years (97.2%, n=634). Females constituted the majority of the participants (69.9%, n=456). Regarding the field of study, the College of Medicine had the highest representation (52.9%, n=345). Regarding body mass index, the normal weight category was the most prevalent, encompassing 59.8% (n=390) of the participants. The results show that the participants generally had a good grade point average (GPA) in the range of 3.50 to 4.00. Also, the time spent on social media applications was not correlated with academic performance (P=0.575). Importantly, the majority of participants perceived that lifestyle habits impacted their academic performance. Conclusion This study found that unhealthy lifestyle factors, such as lack of physical activity, inadequate sleep, poor dietary choices, smoking, and mental health issues such as anxiety, have a negative impact on academic performance. Therefore, the dissemination of relevant knowledge is needed to promote the importance of a healthy lifestyle and raise students' awareness.
Keywords: academic performance; lifestyle factors; saudi arabia; social media; university students.
Copyright © 2024, Mahfouz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Smartphone Addiction Prevalence and Its Association on Academic Performance, Physical Health, and Mental Well-Being among University Students in Umm Al-Qura University (UQU), Saudi Arabia.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 21;19(6):3710. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19063710. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35329397 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Effect of Physical Activity, Nutrition, and Lifestyle Factors on Medical Students' Academic Achievement.Cureus. 2024 Mar 17;16(3):e56343. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56343. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38633916 Free PMC article.
-
Primary headache characters and coping strategies among medical students of Umm Al-Qura University in the Western Region of Saudi Arabia.Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2018 Oct;23(4):308-313. doi: 10.17712/nsj.2018.4.20180256. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2018. PMID: 30351288 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of weight status, dietary habits and beliefs, physical activity, and nutritional knowledge among university students.Perspect Public Health. 2016 Jul;136(4):231-44. doi: 10.1177/1757913915609945. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Perspect Public Health. 2016. PMID: 26475773 Review.
-
The Academic Basis of Lifestyle Medicine.Am J Lifestyle Med. 2023 Dec 6;18(4):497-511. doi: 10.1177/15598276231212825. eCollection 2024 Jul-Aug. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2023. PMID: 39262885 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sociodemographic aspects, beliefs about lifestyles, and religiosity as predictors of life satisfaction in Peruvian university students: a cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2024 Oct 14;12:1476544. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1476544. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39469206 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity levels among college students in Saudi Arabia.Saudi Med J. 2025 Jun;46(6):587-607. doi: 10.15537/smj.2025.46.6.20240073. Saudi Med J. 2025. PMID: 40516939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Literature Review on Optimizing Study Strategies in Medical Education: Insights From Exam Scores and Study Resources.Cureus. 2024 Nov 19;16(11):e74034. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74034. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39712740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Healthy Living: What Is a Healthy Lifestyle? Copenhagen: Regional Office for Europe; 1999. World Health Organization. Regional Office for Europe. (1999). Healthy living : what is a healthy lifestyle?
-
- Relationships between dietary habits and the prevalence of fatigue in medical students. Tanaka M, Mizuno K, Fukuda S, Shigihara Y, Watanabe Y. Nutrition. 2008;24:985–989. - PubMed
-
- Physical activity and academic achievement among the medical students: a cross-sectional study. Al-Drees A, Abdulghani H, Irshad M, Baqays AA, Al-Zhrani AA, Alshammari SA, Alturki NI. Med Teach. 2016;38 Suppl 1:0–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources