Association between Life's Essential 8 and cognitive function: insights from NHANES 2011-2014
- PMID: 38650867
- PMCID: PMC11034366
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1386498
Association between Life's Essential 8 and cognitive function: insights from NHANES 2011-2014
Abstract
Introduction: Life's Essential 8 (LE8) is prompted by the American Heart Association (AHA) to assess cardiovascular health. The association between LE8 and cognitive function in America is unknown. Our study was to investigate the association of LE8 with cognitive function in general adults.
Materials and methods: A total of 2,301 participants were enrolled in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES). LE8 scores (range 0-100) were obtained from measurements based on American Heart Association definitions, divided into health behavior and health factor scores. Cognitive function was assessed by three tests including the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease (CERAD), Animal fluency test (AFT), and Digit Symbol Substitution test (DSST). The multivariable linear regression analysis explored the associations between LE8 and cognitive function. Smooth curve fitting was explored using restricted cubic splines. The inflection point was determined by the two-piecewise linear regression.
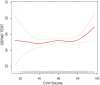
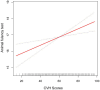
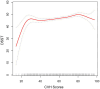
Results: In the multivariable linear regression model with full adjustment for confounding variables, AFT scores were 1.2 points higher in participants with LE8 scores >80 than in those with LE8 scores <50 (high LE8 score group: β = 1.20, 95% CI 0.37, 2.03), and 3.32 points higher in DSST (high LE8 score group: β = 3.32, 95% CI 1.24, 5.39). Although high LE8 scores show a Negative association with high CERAD, we found a significant association between higher LE8 scores and higher CERAD when LE8 scores were higher than 82.5 (β = 0.21 95%CI 0.04, 0.39, p-value = 0.0179).
Conclusion: Our study highlighted a positive association between Life's Essential 8 and cognitive function in older adults.
Keywords: Life’s Essential 8; NHANES; cardiovascular health; cognitive function; older adults.
Copyright © 2024 Liang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Angevaren M., Aufdemkampe G., Verhaar H., Aleman A., Vanhees L. (2008). “Physical activity and enhanced fitness to improve cognitive function in older people without known cognitive impairment” in Cochrane database of systematic reviews. ed. The Cochrane Collaboration (Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; ) - PubMed
-
- Bailey R. L., Jun S., Murphy L., Green R., Gahche J. J., Dwyer J. T., et al. (2020). High folic acid or folate combined with low vitamin B-12 status: potential but inconsistent association with cognitive function in a nationally representative cross-sectional sample of US older adults participating in the NHANES. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 112, 1547–1557. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa239, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

