Epidermal oxysterols function as alarm substances in zebrafish
- PMID: 38650983
- PMCID: PMC11033690
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109660
Epidermal oxysterols function as alarm substances in zebrafish
Abstract
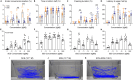
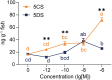
Alarm substances signal imminent predation thread and enable anti-predation strategies. In shoaling fish, alarm cues diffuse from injured skins that induce intense fear and anti-predation behaviors in other members. While these "fear substances" are shown to be present in numerous fishes and thought to exist in roughly 8,000 Ostariophysan species, their chemical nature remains largely unknown. We posited that fish alarm cues comprise small compounds and induce specific behaviors characteristic of fish exposed to skin extracts. Using the behaviors as bioassays, we tracked the alarm function of zebrafish skin extract to two compounds, 24-methyl-5α-cholestane-3α,7α,12α,24,28-pentahydroxy 28-sulfate, an oxysterol sulfate, and 5α-cyprinol sulfate. At concentrations of less than one nanomolar, each compound induced anti-predator behaviors and increased cortisol levels in zebrafish. Their mixture, at the natural ratio, replicated the skin extract in eliciting the full suite of anti-predator behavior patterns. Our findings reveal a molecular mechanism whereby fish escape predation danger.
Keywords: Behavioral neuroscience; Biological sciences; Biomolecules; Neuroscience.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Wyatt T.D. Cambridge University Press; 2014. Pheromones and Animal Behavior: Chemical Signals and Signatures.
-
- Verheggen F.J., Haubruge E., Mescher M.C. In: Vitamins & Hormones. Litwack G., editor. Academic Press; 2010. Alarm pheromones-chemical signaling in response to danger; pp. 215–239. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari M.C., Wisenden B.D., Chivers D.P. Chemical ecology of predator-prey interactions in aquatic ecosystems: a review and prospectus. Can. J. Zool. 2010;88:698–724. doi: 10.1139/z10-029. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

