Mendelian randomization analyses for the causal relationship between early age at first sexual intercourse, early age at first live birth, and postpartum depression in pregnant women
- PMID: 38651010
- PMCID: PMC11033313
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1287934
Mendelian randomization analyses for the causal relationship between early age at first sexual intercourse, early age at first live birth, and postpartum depression in pregnant women
Abstract
Introduction: There are insufficient epidemiological studies on the impact of age at first sexual intercourse (AFS) and age at first live birth (AFB) on postpartum depression (PPD) in pregnant women, and the conclusions of these studies are inconsistent.
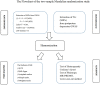
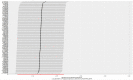
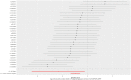
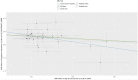
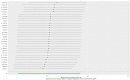
Methods: We performed a Mendelian randomization (MR) study to determine the causal relationship between AFS or AFB and the risk of PPD. The summary data were extracted from genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary datasets. We selected the instrumental variables according to the P value of exposure-related single nucleotide polymorphisms (P<5 ×10-9 for AFS and P<5 ×10-8 for AFB) and estimated the linkage disequilibrium using the clump parameter (10,000 kb, r2 < 0.001). Single nucleotide polymorphisms were considered instrumental variables that were significantly associated with exposure factors without linkage disequilibrium. The F-statistics of the instrumental variables should all be larger than 10. A random-effects model of IVW was constructed as the main method in our study.
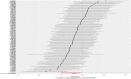
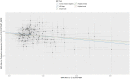
Results and discussion: MR studies based on GWAS data revealed that both AFS (OR = 0.4, P <0.001) and AFB (OR = 0.38, P <0.001) were negatively correlated with the risk of PPD. Early AFS and early AFB should be studied as possible risk factors for PPD in the future. Public health departments should attach importance to sex education for young girls. The results of our TSMR should be verified by high-quality prospective epidemiological studies in the future.
Keywords: age at first birth; age at first sexual intercourse; causal relationship; postpartum depression; sex education.
Copyright © 2024 Zhao and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic liability to age at first sex and birth in relation to cardiovascular diseases: a Mendelian randomization study.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Apr 6;16(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01496-w. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37024926 Free PMC article.
-
Causal relationship between Women's reproductive traits and postpartum depression: a multivariate mendelian randomization analysis.Front Genet. 2024 Oct 11;15:1434762. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1434762. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39464794 Free PMC article.
-
A causal examination of the correlation between hormonal and reproductive factors and low back pain.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 May 10;15:1326761. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1326761. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38800490 Free PMC article.
-
The causal effect of reproductive factors on pelvic floor dysfunction: a Mendelian randomization study.BMC Womens Health. 2024 Jan 28;24(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12905-024-02914-6. BMC Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 38281950 Free PMC article.
-
Association between age at first birth and postpartum depression: A two-sample mendelian randomization analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 27;9(10):e20500. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20500. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37790979 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessing the associations of 1,400 blood metabolites with major depressive disorder: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 6;15:1391535. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1391535. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38903637 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the relationships of 1,400 blood metabolites with abdominal aortic aneurysm: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 3;15:1514293. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1514293. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39830355 Free PMC article.
-
Causal effect of the age at first birth with depression: a mendelian randomization study.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Jul 24;17(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01966-9. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39049090 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially expressed transcripts associated with depressive symptoms during pregnancy and postpartum.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Jun 5. doi: 10.1038/s41380-025-03068-z. Online ahead of print. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40473930
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

