Postmarket safety communications on drugs approved in Japan: A 25-year analysis
- PMID: 38651283
- PMCID: PMC11036129
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.13803
Postmarket safety communications on drugs approved in Japan: A 25-year analysis
Abstract
Drug safety communications (DSCs) are essential tools for communicating important postmarket serious drug safety information to healthcare professionals and patients. Previous studies characterized DSCs issued by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA); however, knowledge about the activities of the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA)/the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW) is limited. This study characterized DSCs by the PMDA/MHLW in comparison with previously reported DSCs by the FDA and the EMA. We retrospectively analyzed 37 DSCs of 41 adverse drug reactions (ADRs) for 33 drugs in Japan from 1997 to 2022. Most DSCs were related to non-oncology drugs (30/37, 81.1%), and the median (interquartile range) time from approval to DSC issuance was 19 (10-51) months. Notably, the regulatory review reports and the latest labels before DSC issuance did not describe 16/28 (57.1%) and 12/37 (32.4%) of the ADRs related to DSCs, respectively. Most DSCs resulted in label revisions (36/37, 97.3%) and seven drugs were eventually withdrawn. Some DSC characteristics are similar among the PMDA/MHLW, the FDA, and the EMA; however, the number, contents, and range of new safety issues addressed by DSCs differ among the three jurisdictions. Our study emphasized the importance of continuous efforts to gather postmarket drug safety information because substantial ADRs that led to DSCs were recognized after approval and were associated with critical label revisions and withdrawals. Future studies are required to address global challenges for regulatory harmonization of safety-related regulatory actions.
© 2024 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures
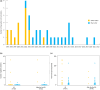
References
-
- Croteau D, Pinnow E, Wu E, Munoz M, Bulatao I, Dal Pan G. Sources of evidence triggering and supporting safety‐related labeling changes: a 10‐year longitudinal assessment of 22 new molecular entities approved in 2008 by the US Food and Drug Administration. Drug Saf. 2022;45:169‐180. doi:10.1007/s40264-021-01142-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Drug Safety Communications (the U.S. Food and Drug Administration). 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug‐safety‐and‐availability/drug‐safety‐commu.... Accessed September 18, 2023.
-
- Direct healthcare professional communications (the European Medicines Agency). 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human‐regulatory/post‐authorisation/pharmac.... Accessed September 18, 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

