Efficient Expression of Functionally Active Aflibercept with Designed N-glycans
- PMID: 38651409
- PMCID: PMC11036266
- DOI: 10.3390/antib13020029
Efficient Expression of Functionally Active Aflibercept with Designed N-glycans
Abstract
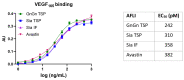
Aflibercept is a therapeutic recombinant fusion protein comprising extracellular domains of human vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs) and IgG1-Fc. It is a highly glycosylated protein with five N-glycosylation sites that might impact it structurally and/or functionally. Aflibercept is produced in mammalian cells and exhibits large glycan heterogeneity, which hampers glycan-associated investigations. Here, we report the expression of aflibercept in a plant-based system with targeted N-glycosylation profiles. Nicotiana benthamiana-based glycoengineering resulted in the production of aflibercept variants carrying designed carbohydrates, namely, N-glycans with terminal GlcNAc and sialic acid residues, herein referred to as AFLIGnGn and AFLISia, respectively. Both variants were transiently expressed in unusually high amounts (2 g/kg fresh leaf material) in leaves and properly assembled to dimers. Mass spectrometric site-specific glycosylation analyses of purified aflibercept showed the presence of two to four glycoforms in a consistent manner. We also demonstrate incomplete occupancy of some glycosites. Both AFLIGnGn and AFLISia displayed similar binding potency to VEGF165, with a tendency of lower binding to variants with increased sialylation. Collectively, we show the expression of functionally active aflibercept in significant amounts with controlled glycosylation. The results provide the basis for further studies in order to generate optimized products in the best-case scenario.
Keywords: Fc fusion; aflibercept; anti VEGF; glycan engineering; glycosylation; plant expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analytical comparability assessment on glycosylation of ziv-aflibercept and the biosimilar candidate.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jun 1;180:494-509. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.020. Epub 2021 Mar 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33684428
-
Site-Specific Glycan Microheterogeneity Evaluation of Aflibercept Fusion Protein by Glycopeptide-Based LC-MSMS Mapping.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 5;23(19):11807. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911807. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233110 Free PMC article.
-
N-glycosylation engineering of plants for the biosynthesis of glycoproteins with bisected and branched complex N-glycans.Glycobiology. 2011 Jun;21(6):813-23. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwr009. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Glycobiology. 2011. PMID: 21317243 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant plant-derived human IgE glycoproteomics.J Proteomics. 2017 May 24;161:81-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 Apr 8. J Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28400175
-
Posttranslational modifications of heterologous proteins expressed in Nicotiana benthamiana.Plant Biotechnol J. 2025 Jun 8. doi: 10.1111/pbi.70176. Online ahead of print. Plant Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40483572 Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing Transient Expression Systems with Plant Viral Vectors for the Production of Biopharmaceuticals in Nicotiana benthamiana.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 9;26(12):5510. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125510. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564973 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wells J.A., Glassman A.R., Ayala A.R., Jampol L.M., Bressler N.M., Bressler S.B., Brucker A.J., Ferris F.L., Hampton G.R., Jhaveri C., et al. Aflibercept, Bevacizumab, or Ranibizumab for Diabetic Macular Edema: Two-Year Results from a Comparative Effectiveness Randomized Clinical Trial. Ophthalmology. 2016;123:1351–1359. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.02.022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

