Monitoring Humoral Response Following BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation Patients: A Single-Center Prospective Study along with a Brief Review of Current Literature
- PMID: 38651451
- PMCID: PMC11036264
- DOI: 10.3390/hematolrep16020022
Monitoring Humoral Response Following BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation Patients: A Single-Center Prospective Study along with a Brief Review of Current Literature
Abstract
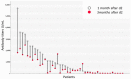
Data on antibody response (AR) after vaccination against SARS-CoV2 in hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation setting (HSCT) were initially scarce, mainly due to the exclusion of such patients from approval studies. Shortly after the worldwide application of vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in vulnerable populations such as patients with hematologic malignancies, limited single-center trials, including HSCT patients, were published. However, there was a great heterogeneity between them regarding the type of underlying malignancy, co-current treatment, type of vaccine, method of AR measurement, and time point of AR measurement. Herein, we present the results of a prospective study on AR after vaccination for SARS-CoV-2 using the BNT162b2 vaccine in a cohort of 54 HSCT recipients-mostly autologous from a single Unit-along with a broad review of the current literature. In our cohort, the AR positivity rate at 1 month was 80.8% and remained positive in 85.7% of patients at 3 months after vaccination. There were only nine non-responders, who were more heavily pretreated and more frequently hypogammaglobulinemic compared to responders. High antibody titers (AT), [AT ≥ 1000 U/mL], were detected in 38.5% and 30.6% of the patients at m1 and m3, respectively. A significant decline in AT between m1 and m3 was demonstrated-p < 0.0001; median AT1 and AT3 were 480.5 and 293 U/mL, respectively. A novel finding of our study was the negative impact of IgA hypogammaglobulinemia on response to vaccination. Other negative significant factors were treatment with anti-CD20 antibody at vaccination and vaccination within 18 months from HSCT. Our data indicate that HSCT recipients elicit a positive response to the BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 when vaccinated at 6 months post-transplant, and vaccination should be offered to this patient population even within the post-pandemic COVID-19 era.
Keywords: BNT162b2 vaccine; COVID-19 pandemic; SARS-CoV-2; autologous transplantation; hematologic malignancies; stem-cell transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Third BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Dose Significantly Enhances Immunogenicity in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Mar 31;11(4):775. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11040775. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37112688 Free PMC article.
-
Specific immune response to mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 in patients receiving allogeneic stem cell transplantation for myeloid malignancy was altered by immunosuppressive therapy.Leuk Res. 2023 Jul;130:107314. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2023.107314. Epub 2023 May 16. Leuk Res. 2023. PMID: 37216792 Free PMC article.
-
B Cell Aplasia Is the Most Powerful Predictive Marker for Poor Humoral Response after BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Transplant Cell Ther. 2022 May;28(5):279.e1-279.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2022.02.018. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022. PMID: 35218998 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 mRNA vaccine and early clinical outcomes in patients with haematological malignancies in Lithuania: a national prospective cohort study.Lancet Haematol. 2021 Aug;8(8):e583-e592. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(21)00169-1. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Lancet Haematol. 2021. PMID: 34224668 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients with Hematological Malignances.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Apr 25;13(5):465. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13050465. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40432077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 Vaccine Experience: Loss of Humoral Response Following Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in Multiple Myeloma Patients and Positive Effect of Booster Dose.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 1;14(13):4648. doi: 10.3390/jcm14134648. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40649022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vijenthira A., Gong I.Y., Fox T.A., Booth S., Cook G., Fattizzo B., Martín-Moro F., Razanamahery J., Riches J.C., Zwicker J., et al. Outcomes of Patients with Hematologic Malignancies and COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 3377 Patients. Blood. 2020;136:2881. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020008824. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sharma A., Bhatt N.S., St Martin A., Abid M.B., Bloomquist J., Chemaly R.F., Dandoy C., Gauthier J., Gowda L., Perales M.A., et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of COVID-19 in Haematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation Recipients: An Observational Cohort Study. Lancet Haematol. 2021;8:e185–e193. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30429-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ljungman P., de la Camara R., Mikulska M., Tridello G., Aguado B., Zahrani M.A., Apperley J., Berceanu A., Bofarull R.M., Calbacho M., et al. COVID-19 and Stem Cell Transplantation; Results from an EBMT and GETH Multicenter Prospective Survey. Leukemia. 2021;35:2885–2894. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01302-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous