MRI in the Evaluation of Cryptogenic Stroke and Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source
- PMID: 38652031
- PMCID: PMC11070612
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.231934
MRI in the Evaluation of Cryptogenic Stroke and Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source
Abstract
Cryptogenic stroke refers to a stroke of undetermined etiology. It accounts for approximately one-fifth of ischemic strokes and has a higher prevalence in younger patients. Embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS) refers to a subgroup of patients with nonlacunar cryptogenic strokes in whom embolism is the suspected stroke mechanism. Under the classifications of cryptogenic stroke or ESUS, there is wide heterogeneity in possible stroke mechanisms. In the absence of a confirmed stroke etiology, there is no established treatment for secondary prevention of stroke in patients experiencing cryptogenic stroke or ESUS, despite several clinical trials, leaving physicians with a clinical dilemma. Both conventional and advanced MRI techniques are available in clinical practice to identify differentiating features and stroke patterns and to determine or infer the underlying etiologic cause, such as atherosclerotic plaques and cardiogenic or paradoxical embolism due to occult pelvic venous thrombi. The aim of this review is to highlight the diagnostic utility of various MRI techniques in patients with cryptogenic stroke or ESUS. Future trends in technological advancement for promoting the adoption of MRI in such a special clinical application are also discussed.
© RSNA, 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



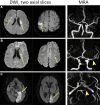

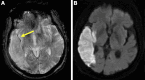
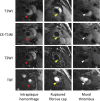
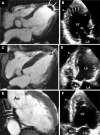


References
-
- Adams HP Jr , Bendixen BH , Kappelle LJ , et al. . Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment . Stroke 1993. ; 24 ( 1 ): 35 – 41 . - PubMed
-
- Elgendy AY , Saver JL , Amin Z , et al. . Proposal for Updated Nomenclature and Classification of Potential Causative Mechanism in Patent Foramen Ovale-Associated Stroke . JAMA Neurol 2020. ; 77 ( 7 ): 878 – 886 . - PubMed
-
- Hart RG , Diener HC , Coutts SB , et al. . Embolic strokes of undetermined source: the case for a new clinical construct . Lancet Neurol 2014. ; 13 ( 4 ): 429 – 438 . - PubMed
-
- Ntaios G . Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source: JACC Review Topic of the Week . J Am Coll Cardiol 2020. ; 75 ( 3 ): 333 – 340 . - PubMed
-
- Hart RG , Sharma M , Mundl H , et al. . Rivaroxaban for Stroke Prevention after Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source . N Engl J Med 2018. ; 378 ( 23 ): 2191 – 2201 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

