Role of the RAAS in mediating the pathophysiology of COVID-19
- PMID: 38652364
- PMCID: PMC11126499
- DOI: 10.1007/s43440-024-00596-3
Role of the RAAS in mediating the pathophysiology of COVID-19
Abstract
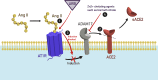
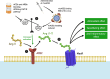
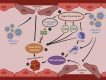
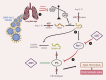
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) holds a position of paramount importance as enzymatic and endocrine homeostatic regulator concerning the water-electrolyte and acid-base balance. Nevertheless, its intricacy is influenced by the presence of various complementary angiotensins and their specific receptors, thereby modifying the primary RAAS actions. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) acts as a surface receptor for SARS-CoV-2, establishing an essential connection between RAAS and COVID-19 infection. Despite the recurring exploration of the RAAS impact on the trajectory of COVID-19 along with the successful resolution of many inquiries, its complete role in the genesis of delayed consequences encompassing long COVID and cardiovascular thrombotic outcomes during the post-COVID phase as well as post-vaccination, remains not fully comprehended. Particularly noteworthy is the involvement of the RAAS in the molecular mechanisms underpinning procoagulant processes throughout COVID-19. These processes significantly contribute to the pathogenesis of organ complications as well as determine clinical outcomes and are discussed in this manuscript.
Keywords: ADAM17; Angiotensin; COVID-19; Coagulation; RAAS; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased complications of COVID-19 in people with cardiovascular disease: Role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) dysregulation.Chem Biol Interact. 2022 Jan 5;351:109738. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109738. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Chem Biol Interact. 2022. PMID: 34740598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).J Pathol. 2020 Jul;251(3):228-248. doi: 10.1002/path.5471. Epub 2020 Jun 10. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32418199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-SARS-CoV axis: a comprehensive review.Eur Respir J. 2020 Jul 9;56(1):2000912. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00912-2020. Print 2020 Jul. Eur Respir J. 2020. PMID: 32341103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2, ACE2 expression, and systemic organ invasion.Physiol Genomics. 2021 Feb 1;53(2):51-60. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00087.2020. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Physiol Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33275540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 pathophysiology may be driven by an imbalance in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 23;12(1):2417. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22713-z. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33893295 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Selected Biochemical Parameters of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Repeat Convalescent Plasma Donors in the Context of Long-Term Changes Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 10;14(14):4910. doi: 10.3390/jcm14144910. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725601 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
