Aspirin versus low-molecular-weight heparin for thromboprophylaxis after orthopaedic surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38652521
- PMCID: PMC11064920
- DOI: 10.1097/MBC.0000000000001300
Aspirin versus low-molecular-weight heparin for thromboprophylaxis after orthopaedic surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
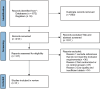
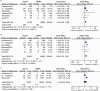
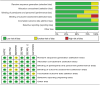
The article aimed to compare the efficiency and safety of aspirin with low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) for thromboprophylaxis in orthopaedic surgery patients. According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, PubMed, Embase and Cochrane Library database were searched for studies comparing aspirin and LMWH in venous thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis until 25 April 2023. The outcome measures included deep venous thrombosis(DVT)/Pulmonary embolism(PE) events, major bleeding events, wound complications, wound infection and death. Six studies met the requirements of our meta-analysis, including 12 470 patients in the aspirin group and 10 857 patients in the LMWH group. The meta-analysis showed that results showed that LMWH was superior to aspirin in preventing VTE events (odds ratio (OR) 1.44, 95% CI 1.24-1.68, P < 0.00001), whereas there was no significant difference between them in bleeding events (OR 0.95, 95% CI 0.86-1.05, P = 0.33), wound complication (OR 0.58, 95% CI 0.28-1.17, P = 0.13), wound infection (OR 1.12, 95% CI 0.86-1.47, P = 0.39) and mortality (OR 1.04, 95% CI 0.70-1.55, P = 0.83). In addition, subgroup analysis showed that compared with aspirin, LMWH was more likely to reduce the incidence of DVT events in orthopaedic surgery patients (OR 1.59, 95% CI 1.33-1.91, P < 0.00001), whereas there was no advantage in reducing the incidence of PE events (OR 1.22, 95% CI 0.62-2.40, P = 0.56). Despite the similar safety profiles, this meta-analysis showed that LMWH was significantly superior to aspirin in thromboprophylaxis after orthopaedic surgery. LMWH was still the first-line drug for thrombosis prevention in patients who underwent major orthopaedic surgeries.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
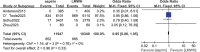
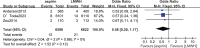
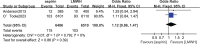
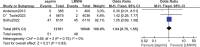
Similar articles
-
Interventions for preventing venous thromboembolism in adults undergoing knee arthroscopy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 6;5(5):CD005259. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005259.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 22;8:CD005259. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005259.pub5. PMID: 32374919 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Prolonged thromboprophylaxis with low molecular weight heparin for abdominal or pelvic surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 27;3(3):CD004318. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004318.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Aug 26;8:CD004318. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004318.pub5. PMID: 30916777 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Prolonged thromboprophylaxis with low molecular weight heparin for abdominal or pelvic surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Aug 26;8(8):CD004318. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004318.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31449321 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged thromboprophylaxis with low molecular weight heparin for abdominal or pelvic surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 27;11(11):CD004318. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004318.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 27;3:CD004318. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004318.pub4. PMID: 30481366 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The efficacy and safety of aspirin in preventing venous thrombosis in major orthopedic surgery: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 20;102(42):e35602. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035602. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37861503 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Majima T, Oshima Y. Venous thromboembolism in major orthopedic surgery. J Nippon Med School 2021; 88:268–272. - PubMed
-
- Stewart DW, Freshour JE. Aspirin for the prophylaxis of venous thromboembolic events in orthopedic surgery patients: a comparison of the AAOS and ACCP guidelines with review of the evidence. Ann Pharmacother 2013; 47:63–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

