Brentuximab vedotin for skin involvement in refractory diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis, an open-label trial
- PMID: 38652570
- PMCID: PMC11879290
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae235
Brentuximab vedotin for skin involvement in refractory diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis, an open-label trial
Abstract
Objective: We explored the efficacy and safety of brentuximab vedotin, a chimeric anti-CD30 antibody drug conjugate, in patients with severe active diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc).
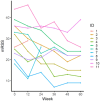
Methods: This phase II proof-of-concept, single centre, open-label, single arm, investigator-initiated trial included patients ≥18 years, with dcSSc, modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS) ≥15 with <5 years since the first non-Raynaud's symptom and/or skin worsening despite immunosuppression who were treated with intravenous brentuximab vedotin 0.6 mg/kg q3 weeks for 45 weeks. The primary end point was a decrease in mRSS of ≥8 points at 48 weeks.
Results: Eleven patients were treated with brentuximab vedotin, with nine completing the study. The mean mRSS reduction at week 48 was 11.3 (95% CI 6.9, 15.8; P = 0.001), meeting the primary end point in the intention to treat analysis (7/11 had a decrease in mRSS ≥8). The % forced vital capacity increased by 7.8% (12.5). The Composite Response Index in dcSSc (CRISS) suggested a beneficial treatment effect (86% ≥0.6). Most adverse events were mild. No SAEs were attributed to brentuximab vedotin.
Conclusion: In dcSSc, brentuximab vedotin improved skin and FVC without safety concerns. A placebo-controlled trial is warranted to corroborate these initial findings.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, http://clinicaltrials.gov, NCT03198689.
Keywords: Systemic sclerosis; biologic; brentuximab; skin; treatment.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Denton CP, Khanna D.. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet (London, England) 2017;390:1685–99. - PubMed
-
- Clements PJ, Hurwitz EL, Wong WK. et al. Skin thickness score as a predictor and correlate of outcome in systemic sclerosis: high-dose versus low-dose penicillamine trial. Arthritis Rheum 2000;43:2445–54. - PubMed
-
- Fernández-Codina A, Walker KM, Pope JE; Scleroderma Algorithm Group. Treatment algorithms for systemic sclerosis according to experts. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, NJ) 2018;70:1820–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical