Systematic characterization of multi-omics landscape between gut microbial metabolites and GPCRome in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 38652661
- PMCID: PMC11968202
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114128
Systematic characterization of multi-omics landscape between gut microbial metabolites and GPCRome in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
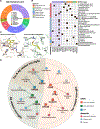
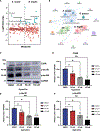
Shifts in the magnitude and nature of gut microbial metabolites have been implicated in Alzheimer's disease (AD), but the host receptors that sense and respond to these metabolites are largely unknown. Here, we develop a systems biology framework that integrates machine learning and multi-omics to identify molecular relationships of gut microbial metabolites with non-olfactory G-protein-coupled receptors (termed the "GPCRome"). We evaluate 1.09 million metabolite-protein pairs connecting 408 human GPCRs and 335 gut microbial metabolites. Using genetics-derived Mendelian randomization and integrative analyses of human brain transcriptomic and proteomic profiles, we identify orphan GPCRs (i.e., GPR84) as potential drug targets in AD and that triacanthine experimentally activates GPR84. We demonstrate that phenethylamine and agmatine significantly reduce tau hyperphosphorylation (p-tau181 and p-tau205) in AD patient induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons. This study demonstrates a systems biology framework to uncover the GPCR targets of human gut microbiota in AD and other complex diseases if broadly applied.
Keywords: AlphaFold2; Alzheimer's disease; CP: Microbiology; CP: Neuroscience; G-protein-coupled receptors; Mendelian randomization; gut microbial metabolite; gut microbiota; machine learning; metabolite-protein interaction; multi-omics; orphan GPCR.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.B.L. has received consulting fees from Vaxxinity and grant support from GE Healthcare and serves on a data safety monitoring board for Eisai.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK120679/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA026938/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG082211/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL147823/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG073323/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG066707/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG076448/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM109025/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG070849/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201500003I/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA024333/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX005976/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- K08 AG065463/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG083003/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG082118/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG063870/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068053/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG074001/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK130227/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG084250/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 GM142002/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201500003C/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS133812/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

