Individual patient data meta-analysis on awake pediatric extracorporeal life support: Feasibility and safety of analgesia, sedation and respiratory support weaning, and physiotherapy
- PMID: 38652693
- PMCID: PMC11849250
- DOI: 10.1177/02676591241240377
Individual patient data meta-analysis on awake pediatric extracorporeal life support: Feasibility and safety of analgesia, sedation and respiratory support weaning, and physiotherapy
Abstract
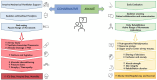
Objective: Awake Extracorporeal Life Support (aECLS) with active mobilization has gained consensus over time, also within the pediatric community. This individual patient data (IPD) meta-analysis summarizes available evidence on pediatric aECLS, its feasibility, and safety regarding sedation weaning, extubation, and physiotherapy.
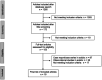
Methods: PubMed/Medline and Cochrane Database were screened until February 2022. Articles reporting on children (≤18 years) undergoing aECLS were selected. IPD were requested, pooled in a single database, and analyzed using descriptive statistics. Primary outcome was survival to hospital discharge. Secondary outcomes included extubation during ECLS, physiotherapy performed, tracheostomy, and complications.
Results: Nineteen articles and 65 patients (males:n = 30/59,50.8%) were included. Age ranged from 2 days to 17 years. ECLS configurations included veno-venous (n = 42/65, 64.6%), veno-arterial (n = 18/65, 27.7%) and other ECLS settings (n = 5/65, 7.7%). Exclusive neck cannulation was performed in 51/65 (78.5%) patients. Extubation or tracheostomy during ECLS was reported in 66.2% (n = 43/65) and 27.7% (n = 18/65) of patients, respectively. Physiotherapy was reported as unspecified physical activity (n = 34/63, 54%), mobilization in bed (n = 15/63, 23.8%), ambulation (n = 14/63, 22.2%). Complications were reported in 60.3% (n = 35/58) of patients, including hemorrhagic (36.2%), mechanical (17.2%), or pulmonary (17.2%) issues, and need for reintubation (15.5%). Survival at discharge was 81.5% (n = 53/65).
Conclusion: Awake ECLS strategy with active physiotherapy can be applied in children from neonatal age. Ambulation is also possible in selected cases. Complications related to such management were limited. Further studies on aECLS are needed to evaluate safety and efficacy of early physiotherapy and define patient selection.
Keywords: analgesia; awake extracorporeal life support; extracorporeal life support; invasive mechanical ventilation; physiotherapy; sedation; single patient meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Roberto Lorusso is a consultant for Medtronic, Getinge, Abiomed and LivaNova, and an Advisory Board Member of Eurosets and Xenios: all honoraria are paid to the University for research support.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Awake extracorporeal life support and physiotherapy in adult patients: A systematic review of the literature.Perfusion. 2023 Jul;38(5):939-958. doi: 10.1177/02676591221096078. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Perfusion. 2023. PMID: 35760523 Free PMC article.
-
Conventional chest physiotherapy compared to other airway clearance techniques for cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 5;5(5):CD002011. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002011.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37144842 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological treatment of children with gastro-oesophageal reflux.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 24;2014(11):CD008550. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008550.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Aug 22;8:CD008550. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008550.pub3. PMID: 25419906 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Cough augmentation techniques for extubation or weaning critically ill patients from mechanical ventilation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 11;1(1):CD011833. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011833.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28075489 Free PMC article.
-
Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) versus nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) for preterm neonates after extubation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 1;2(2):CD003212. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003212.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 27;7:CD003212. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003212.pub4. PMID: 28146296 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources