bDMARD can prevent the progression of AA amyloidosis to end-stage renal disease
- PMID: 38653531
- PMCID: PMC11883751
- DOI: 10.1136/ard-2023-225114
bDMARD can prevent the progression of AA amyloidosis to end-stage renal disease
Abstract
Introduction: AA amyloidosis (AA) can be the consequence of any chronic inflammatory disease. AA is associated with chronic inflammatory diseases (cid+AA), autoinflammatory syndromes (auto+AA) or AA of unknown origin or idiopathic AA (idio+AA). The major organ manifestation is renal AA that can progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and multiple organ failure.
Materials and methods: This study is a monocentric retrospective analysis of the renal outcome and survival of patients with cid+AA (n=34), auto+AA (n=24) and idio+AA (n=25) who were treated with cytokine-inhibiting biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs).
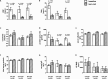
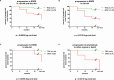
Results: 83 patients with renal AA were identified and followed for a mean observational period of 4.82 years. C reactive protein (CRP), serum amyloid alpha and proteinuria were significantly reduced with bDMARD therapy. Progression to ESRD was prevented in 60% (cid+AA), 88% (auto+AA) and 81% (idio+AA) of patients. Tocilizumab was given to 34 patients with cid+AA and idio+AA and was more effective in reducing CRP and progression to ESRD and death compared with other bDMARDs.
Conclusions: bDMARDs reduce systemic inflammation in various diseases, leading to a reduction of proteinuria and prevention of ESRD. Importantly, tocilizumab was more effective than other bDMARDs in controlling systemic inflammation in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases and idiopathic AA, leading to better renal and overall survival.
Keywords: Amyloidosis; Autoimmune Diseases; Biological Therapy; Familial Mediterranean Fever; Therapeutics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ on behalf of EULAR.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of interleukin-1 inhibitors in familial Mediterranean fever patients complicated with amyloidosis.Mod Rheumatol. 2019 Mar;29(2):363-366. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2018.1457469. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Mod Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 29578360
-
AA amyloidosis complicating the hereditary periodic fever syndromes.Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Apr;65(4):1116-21. doi: 10.1002/art.37827. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 23280696
-
Therapeutic blockade of interleukin-6 by tocilizumab in the management of AA amyloidosis and chronic inflammatory disorders: a case series and review of the literature.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;33(6 Suppl 94):S46-53. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26120866 Review.
-
Renal involvement in systemic amyloidosis: an Italian collaborative study on survival and renal outcome.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008 Mar;23(3):941-51. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm684. Epub 2007 Oct 19. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008. PMID: 17951308
-
Tocilizumab in the treatment of twelve cases with aa amyloidosis secondary to familial mediterranean fever.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017 May 30;12(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0642-0. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017. PMID: 28558744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

